Main Article Content
Abstract
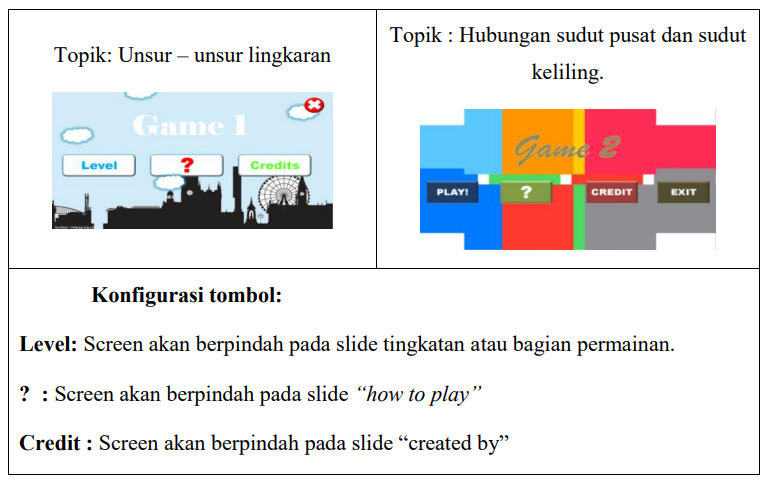
The purpose of this study is to know the implementation, motivation and achievement of the eight grade students of SMP Negeri 1 Tanjung Raja in circle learning through PowerPoint Games. To collect the data observation, questionnaires and tests were used. The result of study showed that the implementation of learning through PowerPoint Games was very successful in terms of teacher’s activities and the activities of the students. In addition, the use of PowerPoint Games motivated students. 19 out of 24 students had very high motivation (79,17%) and 5 out of them had high motivation (20,83%). After using educational games, students outcomes were good in terms of attitudes, skills and knowledge in which the average of percentage was >80% based on the assessment of curriculum 2013.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2017 Sherly Oktaviani, Budi Santoso, Cecil HiltrimartiN

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Beck, L., Fields, T., Fleming, L., Owens, R., & Wilson, C., 2010. Educational Games and Simulations. http://www.slideshare.net/tbfields/educ ational-games-and-simulation. Diakses pada tanggal 12 November 2015.
- Heryaningsih, N. Y., 2013. Upaya Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Siswa dengan Menggunakan Permainan Edukatif pada Topik
- Persamaan Kuadrat di Kelas X-B SMA Adi Luhur Jakarta. Skripsi, Faculty of Education.http://eprints.sampoernauniversity.ac.id/175/. Diakses pada tanggal 17 desember 2015.
- Iskandar. 2009. Psikologi Pendidikan Sebuah Orientasi Baru. Jakarta : Gaung Persada Perss.
- Lamothe, A., 2014. Design Video Games.http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/designing-video- games.html. Diakses pada 29 Maret 2016.
- Malalina dan Kesumawati, N., 2014. Pengembangan Bahan Ajar Interaktif Berbasis Komputer Pokok Bahasan Lingkaran untuk Kelas VIII Sekolah Menengah Pertama. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika Universitas Sriwijaya, 8 (1), 56 – 70.
- NCTM. 2000. Ten General Standards Specified. http://pages.uoregon. edu/moursund/Math/math_ed_goals.ht m#Ten NCTM Standards. Diakses pada 29 Desember 2015.
- NYU. 2013. Educational Video Games Can Boost Motivation to Learn, NYU, CUNY Study Show. https://www.nyu.edu/about/news- publications/news/2013/11/06/educational-video-games-can-boost-motivation-to-learn-nyu- cuny-study-shows-. Diakses pada 9 Mei 2016.
- Polly, D., 2012. Homemade PowerPoint Game. http://wwild.coe.uga. edu/pptgames/teacher.htm. Diakses pada 26 Februari 2016.
- Rofalina, F., 2015. Infografik: Persepsi dan Kebiasaan Belajar Siswa Indonesia. https://www.zenius.net/blog/7420/pers epsi-kebiasaanbelajar-siswa-indonesia. Diakses pada 17 Juni 2016.
- Sari, A. W., 2015. Analisis Kesulitan dalam Pemecahan Masalah MatematikaMateri Lingkaran Menurut Taksonomi Bloom Ditinjau dari Ranah Kognitif pada Siswa Kelas VIII SMP Negeri 4 Tulungagung. Skripsi. IAIN Tulungagung.
- Siko, J. P., dan Barbour, M. K. 2012. Homemade PowerPoint Games: Game Design Pedagogy Aligned to the TPACK Framework. Computers in the Schools, 29(4), 339-354.
- Slavin, R. E. 2005. Educational Psychology Theory and Practice (8th ed). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
- Sumbabi, U. T., dan Bassey, U. A. E., 2013. The Effect of Mathematical Games and Simulations on Senior Secondary School Students Interest in Geometry. Journal of research in national development, 11 (2), 330 – 337.
- Sunzuma, G., Masocha, M., dan Zezekwa, N., 2013. Secondary School Students’ Attitudes Towards their Learning of Geometry: a Survey of Bindura Urban Secondary Schools. Greener Journal of Educational Research, 3 (8), pp. 402-410.
References
Beck, L., Fields, T., Fleming, L., Owens, R., & Wilson, C., 2010. Educational Games and Simulations. http://www.slideshare.net/tbfields/educ ational-games-and-simulation. Diakses pada tanggal 12 November 2015.
Heryaningsih, N. Y., 2013. Upaya Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Siswa dengan Menggunakan Permainan Edukatif pada Topik
Persamaan Kuadrat di Kelas X-B SMA Adi Luhur Jakarta. Skripsi, Faculty of Education.http://eprints.sampoernauniversity.ac.id/175/. Diakses pada tanggal 17 desember 2015.
Iskandar. 2009. Psikologi Pendidikan Sebuah Orientasi Baru. Jakarta : Gaung Persada Perss.
Lamothe, A., 2014. Design Video Games.http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/designing-video- games.html. Diakses pada 29 Maret 2016.
Malalina dan Kesumawati, N., 2014. Pengembangan Bahan Ajar Interaktif Berbasis Komputer Pokok Bahasan Lingkaran untuk Kelas VIII Sekolah Menengah Pertama. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika Universitas Sriwijaya, 8 (1), 56 – 70.
NCTM. 2000. Ten General Standards Specified. http://pages.uoregon. edu/moursund/Math/math_ed_goals.ht m#Ten NCTM Standards. Diakses pada 29 Desember 2015.
NYU. 2013. Educational Video Games Can Boost Motivation to Learn, NYU, CUNY Study Show. https://www.nyu.edu/about/news- publications/news/2013/11/06/educational-video-games-can-boost-motivation-to-learn-nyu- cuny-study-shows-. Diakses pada 9 Mei 2016.
Polly, D., 2012. Homemade PowerPoint Game. http://wwild.coe.uga. edu/pptgames/teacher.htm. Diakses pada 26 Februari 2016.
Rofalina, F., 2015. Infografik: Persepsi dan Kebiasaan Belajar Siswa Indonesia. https://www.zenius.net/blog/7420/pers epsi-kebiasaanbelajar-siswa-indonesia. Diakses pada 17 Juni 2016.
Sari, A. W., 2015. Analisis Kesulitan dalam Pemecahan Masalah MatematikaMateri Lingkaran Menurut Taksonomi Bloom Ditinjau dari Ranah Kognitif pada Siswa Kelas VIII SMP Negeri 4 Tulungagung. Skripsi. IAIN Tulungagung.
Siko, J. P., dan Barbour, M. K. 2012. Homemade PowerPoint Games: Game Design Pedagogy Aligned to the TPACK Framework. Computers in the Schools, 29(4), 339-354.
Slavin, R. E. 2005. Educational Psychology Theory and Practice (8th ed). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Sumbabi, U. T., dan Bassey, U. A. E., 2013. The Effect of Mathematical Games and Simulations on Senior Secondary School Students Interest in Geometry. Journal of research in national development, 11 (2), 330 – 337.
Sunzuma, G., Masocha, M., dan Zezekwa, N., 2013. Secondary School Students’ Attitudes Towards their Learning of Geometry: a Survey of Bindura Urban Secondary Schools. Greener Journal of Educational Research, 3 (8), pp. 402-410.