Main Article Content
Abstract
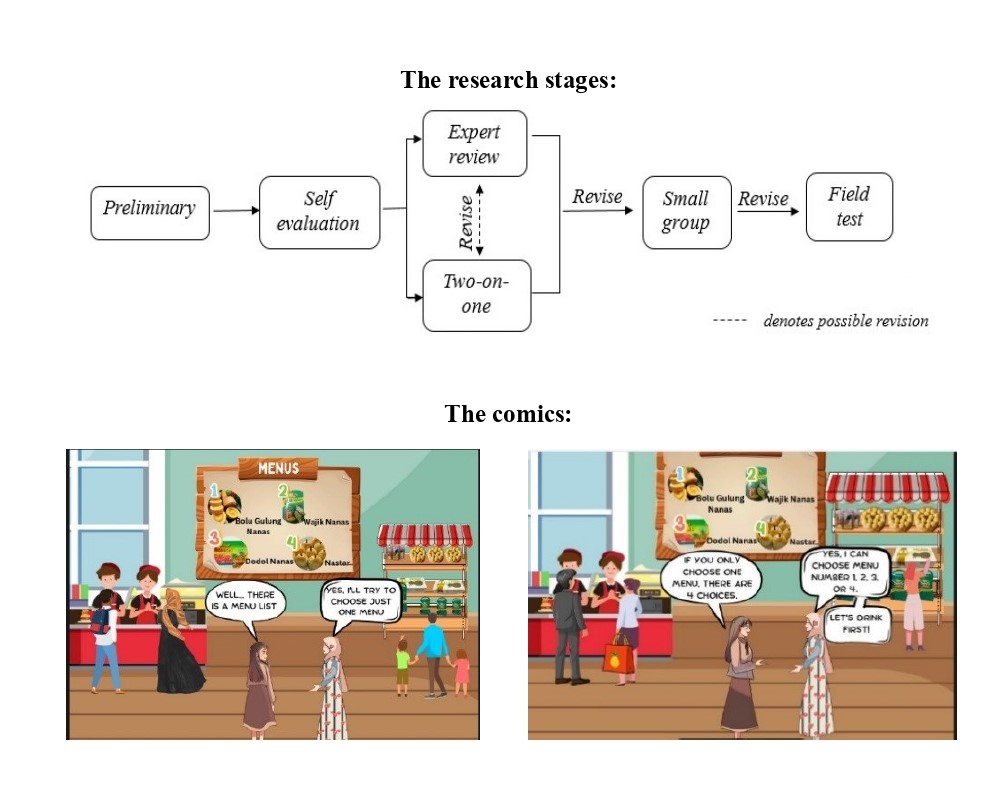
Numerous studies have shown that students face difficulties in learning probability. This study aimed to enhance students’ understanding of the concept of probability while developing their reasoning skills by integrating comics into student worksheets. It focused on designing probability material for grade 10 using the student worksheets and microlearning (comics) that were both effective and efficient. The material was developed using Pendidikan Matematika Realistik Indonesia (PMRI) approach, incorporating a microlearning method within the context of culinary tourism, to enhance students’ understanding of probability and reasoning skills. This study employed a design research methodology in two stages, namely preliminary study and formative evaluation. The subjects of this study were 34 students of grade tenth at Senior High School in Prabumulih. Data collected through observations, tests, and interviews were analyzed descriptively. The study resulted the student worksheets on probability, which were incorporated with microlearning comics whose effectiveness and efficiency were aligned with the characteristics of the PMRI approach. Based on the findings, it can be concluded that the PMRI-based student worksheets that were incorporated with microlearning comics were efficient and effective in helping students develop their reasoning skills. The integration of comics and the PMRI approach reflects a commitment to innovation and the continuous development of effective learning designs that promote inclusive, equitable, and meaningful learning experiences.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2025 Novi Komariyatiningsih, Yusuf Hartono, Ratu Ilma Indra Putri, Cecil Hiltrimartin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Aldosemani, T. I. (2019). Microlearning for macro-outcomes: students’ perceptions of telegram as a microlearning tool. In Lecture Notes in Educational Technology. Springer: Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7361-9_13
- Álvarez, R., Carmen, A., & María, B. (2024). Probabilistic literacy and reasoning of prospective secondary school teachers when interpreting media news. ZDM – Mathematics Education 56:1045–1058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-024-01586-8
- Arican, M., & Kuzu, O. (2019). Diagnosing Preservice Teachers _ Understanding of Statistics and Probability : Developing a Test for Cognitive Assessment. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-019-09985-0
- Arifin, S., Zulkardi, Putri, R.I.I., & Hartono, Y. (2021). On creativity through mathematization in solving non-routine problems. Journal on Mathematics Education, 12(2), 313-330. http://doi.org/10.22342/jme.12.2.13885.313-330
- Armiati, Fauzan, A., Harisman, Y., & Sya’Bani, F. (2022). Local instructional theory of probability topics based on realistic mathematics education for eight-grade students. Journal on Mathematics Education, 13(4), 703–722. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v13i4.pp703-722
- Astuti, D., Anggraeni, L., & Setyawan, F. (2020). Mathematical probability: Student’s misconception in higher education. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1613(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1613/1/012009
- BSKAP. (2024). Decree of the Head of the Education Standards, Curriculum, and Assessment Agency of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology Number 032/H/KR/2024 concerning Learning Achievements in Early Childhood, Elementary Education Level, and Secondary Education Level in the Independent Curriculum. In Kemendikbudristek BSKAP RI.
- Batanero, C., & Álvarez, R. (2024). Teaching and learning of probability. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 56(1), 5–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-023-01511-5
- Bakker, A. (2004). Design research in statistics education on symbolizing and computer tools. [Doctoral thesis 1 (Research UU / Graduation UU), Utrecht University]. Freudenthal Institute. https://dspace.library.uu.nl/handle/1874/893
- Dolasinski, M. J., & Reynolds, J. (2020). Microlearning: A New Learning Model. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research, 44(3), 551–561. https://doi.org/10.1177/1096348020901579
- Greenwood, D., Wooley, S., Vaughan, J., Frank, F., Goodman,J., & Robertson, D. (2011). Essential Mathematics for The Australian Curriculum Year 9. Australia: Cambridge University Press.
- Groove, M. (2018). Math in Focus Mathematics Extention 1. Australia: Copyright Agency Limited.
- Hiltrimartin, C., Hartono, Y., & Indaryanti, I. (2022). Development of Student Activities in Algebra based on Problem Solving in Middle School. Proceedings of the 2nd National Conference on Mathematics Education 2021 (NaCoME 2021), 656(NaCoME 2021), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.220403.008
- Lam, T. O. H. T., Pien, C. L., Hean, L. I. M. L., & Ming, L. I. M. K. (2023). Comicss for Mathematics Instruction for Future-Ready Learners. 4(2), 165–178. https://ame.org.sg/2023/09/06/tme2023-vol-4-no-2-pp-165-178
- Malalina, Indra Putri, R. I., Zulkardi, & Hartono, Y. (2024). Developing mathematics teaching materials using maritime context for higher-order thinking in junior high school. Journal on Mathematics Education, 15(1), 173–190. http://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v15i1.pp173-190
- McNeill, L., & Fitch, D. (2023). Microlearning through the Lens of Gagne’s Nine Events of Instruction: A Qualitative Study. TechTrends, 67(3), 521–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-022-00805-x
- OECD (2023), PISA 2022 Results (Volume I): The State of Learning and Equity in Education, PISA, OECD Publishing, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/53f23881-en
- Pascucci, A. (2024). Probability Theory I. Italy: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63190-0.
- Tessmer M. (1993). Planning and Conducting Formative Evaluation. In London, Philadelphia:Kogan Page. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203061978
- Sari, D. L., Fitriani, D. A., Khaeriyah, D. Z., Hartono, & Nursyahidah, F. (2022). Hypothetical learning trajectory on probability material: The context of the traditional dragon snake toy. 11(2), 203–214. http://journal.institutpendidikan.ac.id/index.php/mosharafa
- Sharma, S., Sharma, S., Doyle, P., Marcelo, L., & Kumar, D. (2021). Teaching and learning probability using games: A systematic review of research from 2010–2020. Waikato Journal of Education, 26(2), 51–64. https://doi.org/10.15663/wje.v26i2.881
- Waheed, H., Hassan, S., Nawaz, R., Aljohani, N. R., & Chen, G. (2023). Early prediction of learners at risk in self-paced education : A neural network approach. Expert Systems With Applications, 213(PA), 118868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118868
- Wijaya, A., Elmaini, & Doorman, M. (2021). A learning trajectory for probability: A case of game-based learning. Journal on Mathematics Education, 12(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.22342/JME.12.1.12836.1-16
- Wijaya, T. T., Hidayat, W., Hermita, N., Alim, J. A., & Talib, C. A. (2024). Exploring contributing factors to PISA 2022 mathematics achievement: Insights from Indonesian teachers. Infinity, 13(1), 139-156. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p139-156
- Zulkardi. (2002). Developing a learning environment on realistic mathematics education for Indonesian student teachers. PrintPartners Ipskamp. https://ris.utwente.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/6073266/thesis_Zulkardi.pdf
- Zulkardi, Putri, R. I. indra, & Wijaya, A. (2020). Two decades of realistic mathematics education in Indonesia. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20223-1_18
- Zulkardi, Z., & Putri, R. I. I. (2020). Supporting Mathematics Teachers to Develop Jumping Task Using PISA Framework (JUMPISA). Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(2), 199–210. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.2.12115.199-210
References
Aldosemani, T. I. (2019). Microlearning for macro-outcomes: students’ perceptions of telegram as a microlearning tool. In Lecture Notes in Educational Technology. Springer: Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7361-9_13
Álvarez, R., Carmen, A., & María, B. (2024). Probabilistic literacy and reasoning of prospective secondary school teachers when interpreting media news. ZDM – Mathematics Education 56:1045–1058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-024-01586-8
Arican, M., & Kuzu, O. (2019). Diagnosing Preservice Teachers _ Understanding of Statistics and Probability : Developing a Test for Cognitive Assessment. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-019-09985-0
Arifin, S., Zulkardi, Putri, R.I.I., & Hartono, Y. (2021). On creativity through mathematization in solving non-routine problems. Journal on Mathematics Education, 12(2), 313-330. http://doi.org/10.22342/jme.12.2.13885.313-330
Armiati, Fauzan, A., Harisman, Y., & Sya’Bani, F. (2022). Local instructional theory of probability topics based on realistic mathematics education for eight-grade students. Journal on Mathematics Education, 13(4), 703–722. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v13i4.pp703-722
Astuti, D., Anggraeni, L., & Setyawan, F. (2020). Mathematical probability: Student’s misconception in higher education. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1613(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1613/1/012009
BSKAP. (2024). Decree of the Head of the Education Standards, Curriculum, and Assessment Agency of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology Number 032/H/KR/2024 concerning Learning Achievements in Early Childhood, Elementary Education Level, and Secondary Education Level in the Independent Curriculum. In Kemendikbudristek BSKAP RI.
Batanero, C., & Álvarez, R. (2024). Teaching and learning of probability. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 56(1), 5–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-023-01511-5
Bakker, A. (2004). Design research in statistics education on symbolizing and computer tools. [Doctoral thesis 1 (Research UU / Graduation UU), Utrecht University]. Freudenthal Institute. https://dspace.library.uu.nl/handle/1874/893
Dolasinski, M. J., & Reynolds, J. (2020). Microlearning: A New Learning Model. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research, 44(3), 551–561. https://doi.org/10.1177/1096348020901579
Greenwood, D., Wooley, S., Vaughan, J., Frank, F., Goodman,J., & Robertson, D. (2011). Essential Mathematics for The Australian Curriculum Year 9. Australia: Cambridge University Press.
Groove, M. (2018). Math in Focus Mathematics Extention 1. Australia: Copyright Agency Limited.
Hiltrimartin, C., Hartono, Y., & Indaryanti, I. (2022). Development of Student Activities in Algebra based on Problem Solving in Middle School. Proceedings of the 2nd National Conference on Mathematics Education 2021 (NaCoME 2021), 656(NaCoME 2021), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.220403.008
Lam, T. O. H. T., Pien, C. L., Hean, L. I. M. L., & Ming, L. I. M. K. (2023). Comicss for Mathematics Instruction for Future-Ready Learners. 4(2), 165–178. https://ame.org.sg/2023/09/06/tme2023-vol-4-no-2-pp-165-178
Malalina, Indra Putri, R. I., Zulkardi, & Hartono, Y. (2024). Developing mathematics teaching materials using maritime context for higher-order thinking in junior high school. Journal on Mathematics Education, 15(1), 173–190. http://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v15i1.pp173-190
McNeill, L., & Fitch, D. (2023). Microlearning through the Lens of Gagne’s Nine Events of Instruction: A Qualitative Study. TechTrends, 67(3), 521–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-022-00805-x
OECD (2023), PISA 2022 Results (Volume I): The State of Learning and Equity in Education, PISA, OECD Publishing, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/53f23881-en
Pascucci, A. (2024). Probability Theory I. Italy: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63190-0.
Tessmer M. (1993). Planning and Conducting Formative Evaluation. In London, Philadelphia:Kogan Page. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203061978
Sari, D. L., Fitriani, D. A., Khaeriyah, D. Z., Hartono, & Nursyahidah, F. (2022). Hypothetical learning trajectory on probability material: The context of the traditional dragon snake toy. 11(2), 203–214. http://journal.institutpendidikan.ac.id/index.php/mosharafa
Sharma, S., Sharma, S., Doyle, P., Marcelo, L., & Kumar, D. (2021). Teaching and learning probability using games: A systematic review of research from 2010–2020. Waikato Journal of Education, 26(2), 51–64. https://doi.org/10.15663/wje.v26i2.881
Waheed, H., Hassan, S., Nawaz, R., Aljohani, N. R., & Chen, G. (2023). Early prediction of learners at risk in self-paced education : A neural network approach. Expert Systems With Applications, 213(PA), 118868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118868
Wijaya, A., Elmaini, & Doorman, M. (2021). A learning trajectory for probability: A case of game-based learning. Journal on Mathematics Education, 12(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.22342/JME.12.1.12836.1-16
Wijaya, T. T., Hidayat, W., Hermita, N., Alim, J. A., & Talib, C. A. (2024). Exploring contributing factors to PISA 2022 mathematics achievement: Insights from Indonesian teachers. Infinity, 13(1), 139-156. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p139-156
Zulkardi. (2002). Developing a learning environment on realistic mathematics education for Indonesian student teachers. PrintPartners Ipskamp. https://ris.utwente.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/6073266/thesis_Zulkardi.pdf
Zulkardi, Putri, R. I. indra, & Wijaya, A. (2020). Two decades of realistic mathematics education in Indonesia. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20223-1_18
Zulkardi, Z., & Putri, R. I. I. (2020). Supporting Mathematics Teachers to Develop Jumping Task Using PISA Framework (JUMPISA). Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(2), 199–210. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.2.12115.199-210