Main Article Content
Abstract
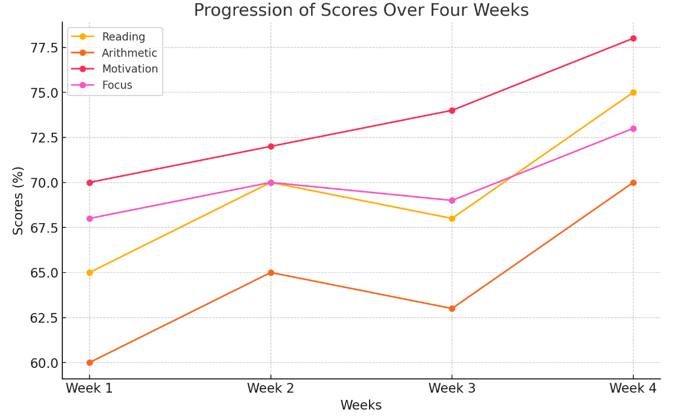
This study aimed to develop a Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) for mathematics learning tailored to children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) at a special needs school in Jambi, utilizing the Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation (ADDIE) model. It focused on enhancing the learning experiences and outcomes for ASD students in a specialized education setting. In the Analysis phase, the needs and challenges of ASD students in learning mathematics were identified through observations, interviews, and literature review. The Design phase involved creating a detailed blueprint for the VLE, emphasizing interactive and user-friendly features. During the Development phase, the VLE was developed incorporating multimedia elements to engage students effectively. The Implementation phase included deploying the VLE in the classroom and training teachers and students to use the system. The Evaluation phase assessed the VLE's effectiveness through metrics such as visual, verbal, auditory, writing, motor, and emotional activities over four meetings. Results showed consistent improvements in all activities, particularly visual, auditory, writing, and motor activities, demonstrating significant enhancements in student engagement and understanding of mathematical concepts. This research underscores the importance of a structured development process and the positive impact of technology-enhanced learning environments on students with ASD.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2025 Kamid, Khairul Anwar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Ahmad, N. L., Yahaya, R., Wahid, H. A., & Fazil, N. S. M. (2023). Role of social factors, self-efficacy and technological support on the use of virtual learning environment among teachers. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 12(1), 369. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v12i1.22628
- Bailey, B., Arciuli, J., & Stancliffe, R. J. (2017). Effects of ABRACADABRA literacy instruction on children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Educational Psychology, 109(2), 257-268. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000138
- Baron-Cohen, S. (2023). Theory of mind and autism: A fifteen year review. In S. Baron-Cohen, H. Tager-Flusberg, & D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Understanding other minds: Perspectives from developmental cognitive neuroscience (pp. 3-20). Oxford Academic. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198524465.003.0001
- Bellini, S., & Akullian, J. (2007). A meta-analysis of video modeling and video self-modeling interventions for children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Exceptional Children, 73(3), 264-287. https://doi.org/10.1177/001440290707300301
- Ben-Sasson, A., Hen, L., Fluss, R., Cermak, S. A., Engel-Yeger, B., & Gal, E. (2009). A meta-analysis of sensory modulation symptoms in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-008-0593-3
- Blatt, G. J. (2012). The neuropathology of autism. Scientifica, 2012(1). https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/703675
- Boon, R. T., Urton, K., Grünke, M., & Ko, E. H. (2020). Video modeling interventions for students with learning disabilities: a systematic review. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 18(1), 49-69.
- Bosseler, A., & Massaro, D. W. (2003). Development and evaluation of a computer-animated tutor for vocabulary and language learning in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33, 653-672. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JADD.0000006002.82367.4f
- Bouck, E. C., & Flanagan, S. (2009). Assistive technology and mathematics: What is there and where can we go in special education. Journal of Special Education Technology, 24(2), 17-30. https://doi.org/10.1177/016264340902400202
- Branch, R. M. (2009). Instructional design: The ADDIE approach. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09506-6
- Brentani, H., de Paula, C. S., Bordini, D., Rolim, D., Sato, F., Portolese, J., Pacifico, M. C., & McCracken, J. T. (2013). Autism spectrum disorders: An overview on diagnosis and treatment. Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry, 35, 62-72. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-4446-2013-S104
- Cardon, T. A. (2016). Technology and the treatment of children with autism spectrum disorder. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20872-5
- Charlop‐Christy, M. H., Carpenter, M., Le, L., LeBlanc, L. A., & Kellet, K. (2002). Using the picture exchange communication system (pecs) with children with autism: Assessment of pecs acquisition, speech, social‐communicative behavior, and problem behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 35(3), 213–231. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2002.35-213
- Chen, S. H. A., & Bernard-Opitz, V. (1993). Comparison of personal and computer-assisted instruction for children with autism. Mental Retardation, 31(6), 368–376. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8152382
- Cheng, S. C., & Lai, C. L. (2020). Facilitating learning for students with special needs: A review of technology-supported special education studies. Journal of Computers in Education, 7, 131-153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-019-00150-8
- Cooper, R. (2017). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM). Knowledge Organization, 44(8), 668-676. https://doi.org/10.5771/0943-7444-2017-8-668
- Delano, M. E. (2007). Video modeling interventions for individuals with autism. Remedial and Special Education, 28(1), 33-42. https://doi.org/10.1177/07419325070280010401
- Fage, C., Consel, C. Y., Balland, E., Etchegoyhen, K., Amestoy, A., Bouvard, M., & Sauzéon, H. (2018). Tablet apps to support first school inclusion of children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in mainstream classrooms: A pilot study. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02020
- Fleury, V. P., Hedges, S., Hume, K., Browder, D. M., Thompson, J. L., Fallin, K., El Zein, F., Reutebuch, C. K., & Vaughn, S. (2014). Addressing the academic needs of adolescents with autism spectrum disorder in secondary education. Remedial and Special Education, 35(2), 68-79. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932513518823
- Gilal, N. G., Zhang, J., & Gilal, F. G. (2018). The four-factor model of product design: scale development and validation. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 27(6), 684-700. https://doi.org/10.1108/jpbm-11-2017-1659
- Gelbar, N. W., Anderson, C., Mccarthy, S., & Buggey, T. (2012). Video self-modeling as an intervention strategy for individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Psychology in the Schools, 49(1), 15-22. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.20628
- Gevarter, C., Bryant, D. P., Bryant, B., Watkins, L., Zamora, C., & Sammarco, N. (2016). Mathematics interventions for individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Review Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 3, 224-238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40489-016-0078-9
- Hewagamage, K. P., Nishakumari, K. M. G. B., & Wikramanayake, G. (2011). Developing online virtual community by facilitating student discussions. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 1(4), 303-308. https://doi.org/10.7763/ijiet.2011.v1.49
- Itskovich, E., Zyga, O., Libove, R. A., Phillips, J. M., Garner, J. P., & Parker, K. J. (2021). Complex interplay between cognitive ability and social motivation in predicting social skill: A unique role for social motivation in children with autism. Autism Research, 14(1), 86-92. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2409
- King, S. A., Lemons, C. J., & Davidson, K. A. (2016). Math interventions for students with autism spectrum disorder: A best-evidence synthesis. Exceptional Children, 82(4) 443-462. https://doi.org/10.1177/0014402915625066
- Koegel, R. L., Koegel, L. K., Vernon, T. W., & Brookman-Frazee, L. I. (2010). Empirically supported pivotal response treatment for children with autism spectrum disorders. In J. R. Weisz & A.E. Kazdin (Eds.), Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (2nd ed., pp. 327-344). The Guilford Press.
- Koller, H. P. (2012). Visual processing and learning disorders. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology, 25(2), 377-383. https://doi.org/10.1097/ICU.0b013e32835720e2
- Mayer, R. E., & Sims, V. K. (1994). For whom is a picture worth a thousand words? Extensions of a dual-coding theory of multimedia learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 86(3), 389-401. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.86.3.389
- McMahon, J., & Cullinan, V. (2014). Education programmes for young children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An evaluation framework. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 35(12), 3689-3697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.09.004
- Miller, N., Wyatt, J., Casey, L. B., & Smith, J. B. (2018). Using computer-assisted instruction to increase the eye gaze of children with autism. Behavioral Interventions, 33(1), 3-12. https://doi.org/10.1002/bin.1507
- Moore, D., McGrath, P., & Thorpe, J. (2000). Computer-aided learning for people with autism - A framework for research and development. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 37(3), 218-228. https://doi.org/10.1080/13558000050138452
- Moore, M., & Calvert, S. (2000). Brief report: Vocabulary acquisition for children with autism: Teacher or computer instruction. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 359-362 https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005535602064
- Najdowski, A. C., Gould, E. R., Lanagan, T. M., & Bishop, M. R. (2014). Designing curriculum programs for children with autism. In J. Tarbox, D. R. Dixon, P. Sturmey, & J. L. Matson (Eds.), Handbook of early intervention for autism spectrum disorders (pp. 179-204). Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0401-3_10
- Odom, S. L., Collet-Klingenberg, L., Rogers, S. J., & Hatton, D. D. (2010). Evidence-based practices in interventions for children and youth with autism spectrum disorders. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 54(4), 275-282. https://doi.org/10.1080/10459881003785506
- Park, M. N., Moulton, E. E., & Laugeson, E. A. (2023). Parent-assisted social skills training for children with autism spectrum disorder: PEERS for preschoolers. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 38(2), 80-89. https://doi.org/10.1177/10883576221110158
- Parsons, S., & Cobb, S. (2011). State-of-the-art of virtual reality technologies for children on the autism spectrum. European Journal of Special Needs Education, 26(3), 355-366. https://doi.org/10.1080/08856257.2011.593831
- Pennington, R. C. (2010). Computer-assisted instruction for teaching academic skills to students with autism spectrum disorders: A review of literature. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 25(4), 239-248. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088357610378291
- Pertiwi, L. K., & Djoehaeni, H. (2021, March). Analysis of early childhood tutorial content to improve reading, writing, and arithmetic skills [Paper presentation]. In Advances in social science, education and humanities research. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Early Childhood Education (ICECE 2020) (pp. 130-135). Atlantis Press. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.210322.028
- Plass, J. L., Chun, D. M., Mayer, R. E., & Leutner, D. (1998). Supporting visual and verbal learning preferences in a second-language multimedia learning environment. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(1), 25-36. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.90.1.25
- Ramdoss, S., MacHalicek, W., Rispoli, M., Mulloy, A., Lang, R., & O’Reilly, M. (2012). Computer-based interventions to improve social and emotional skills in individuals with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Developmental Neurorehabilitation, 15(2), 119-135. https://doi.org/10.3109/17518423.2011.651655
- Ramli, J. A., & Surbaini, K. N. (2023). Assessing personal attributes and virtual learning engagement during pandemic among accounting undergraduates. In A. H. Jaaffar, S. Buniamin, N. R. A. Rahman, N. S. Othman, N. Mohammad, S. Kasavan, N. E. A. B. Mohamad, Z. M. Saad, F. A. Ghani, & N. I. N. Redzuan (Eds.), Accelerating Transformation towards Sustainable and Resilient Business: Lessons Learned from the COVID-19 Crisis, vol 1. European Proceedings of Finance and Economics (pp. 982-990). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epfe.23081.91
- Ring, E., & Prunty, A. (2012). Adapting the curriculum to include learners with autistic spectrum disorders in Irish schools. In Special and Inclusive Education: A Research Perspective (Vol. 9783034308762, pp. 289-302). Peter Lang Publishing Group.
- Sansosti, F. J., & Powell-Smith, K. A. (2008). Using computer-presented social stories and video models to increase the social communication skills of children with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 10(3), 162-178. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300708316259
- Shin, M., Park, J., Grimes, R., & Bryant, D. P. (2021). Effects of using virtual manipulatives for students with disabilities: Three-level multilevel modeling for single-case data. Exceptional Children, 87(4), 418-437. https://doi.org/10.1177/00144029211007150
- Strickland, D. (1996). A virtual reality application with autistic children. Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, 5(3), 319-329. https://doi.org/10.1162/pres.1996.5.3.319
- Subandi, I. P. and Hidayah, R. (2023). Validity of electronic student worksheets to improve students' metacognitive skills through pbl on petroleum materials. Hydrogen: Jurnal Kependidikan Kimia, 11(4), 391-400. https://doi.org/10.33394/hjkk.v11i4.8236
- Tuedor, M., Franco, F., White, A., Smith, S., & Adams, R. (2019). Testing literacy educational software to develop design guidelines for children with autism. International Journal of Disability, Development and Education, 66(1), 19-35. https://doi.org/10.1080/1034912X.2018.1450494
- Viljaranta, J., Lerkkanen, M. K., Poikkeus, A. M., Aunola, K., & Nurmi, J. E. (2009). Cross-lagged relations between task motivation and performance in arithmetic and literacy in kindergarten. Learning and Instruction, 19(4), 335-344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.06.011
References
Ahmad, N. L., Yahaya, R., Wahid, H. A., & Fazil, N. S. M. (2023). Role of social factors, self-efficacy and technological support on the use of virtual learning environment among teachers. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 12(1), 369. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v12i1.22628
Bailey, B., Arciuli, J., & Stancliffe, R. J. (2017). Effects of ABRACADABRA literacy instruction on children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Educational Psychology, 109(2), 257-268. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000138
Baron-Cohen, S. (2023). Theory of mind and autism: A fifteen year review. In S. Baron-Cohen, H. Tager-Flusberg, & D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Understanding other minds: Perspectives from developmental cognitive neuroscience (pp. 3-20). Oxford Academic. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198524465.003.0001
Bellini, S., & Akullian, J. (2007). A meta-analysis of video modeling and video self-modeling interventions for children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Exceptional Children, 73(3), 264-287. https://doi.org/10.1177/001440290707300301
Ben-Sasson, A., Hen, L., Fluss, R., Cermak, S. A., Engel-Yeger, B., & Gal, E. (2009). A meta-analysis of sensory modulation symptoms in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-008-0593-3
Blatt, G. J. (2012). The neuropathology of autism. Scientifica, 2012(1). https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/703675
Boon, R. T., Urton, K., Grünke, M., & Ko, E. H. (2020). Video modeling interventions for students with learning disabilities: a systematic review. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 18(1), 49-69.
Bosseler, A., & Massaro, D. W. (2003). Development and evaluation of a computer-animated tutor for vocabulary and language learning in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33, 653-672. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JADD.0000006002.82367.4f
Bouck, E. C., & Flanagan, S. (2009). Assistive technology and mathematics: What is there and where can we go in special education. Journal of Special Education Technology, 24(2), 17-30. https://doi.org/10.1177/016264340902400202
Branch, R. M. (2009). Instructional design: The ADDIE approach. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09506-6
Brentani, H., de Paula, C. S., Bordini, D., Rolim, D., Sato, F., Portolese, J., Pacifico, M. C., & McCracken, J. T. (2013). Autism spectrum disorders: An overview on diagnosis and treatment. Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry, 35, 62-72. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-4446-2013-S104
Cardon, T. A. (2016). Technology and the treatment of children with autism spectrum disorder. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20872-5
Charlop‐Christy, M. H., Carpenter, M., Le, L., LeBlanc, L. A., & Kellet, K. (2002). Using the picture exchange communication system (pecs) with children with autism: Assessment of pecs acquisition, speech, social‐communicative behavior, and problem behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 35(3), 213–231. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2002.35-213
Chen, S. H. A., & Bernard-Opitz, V. (1993). Comparison of personal and computer-assisted instruction for children with autism. Mental Retardation, 31(6), 368–376. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8152382
Cheng, S. C., & Lai, C. L. (2020). Facilitating learning for students with special needs: A review of technology-supported special education studies. Journal of Computers in Education, 7, 131-153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-019-00150-8
Cooper, R. (2017). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM). Knowledge Organization, 44(8), 668-676. https://doi.org/10.5771/0943-7444-2017-8-668
Delano, M. E. (2007). Video modeling interventions for individuals with autism. Remedial and Special Education, 28(1), 33-42. https://doi.org/10.1177/07419325070280010401
Fage, C., Consel, C. Y., Balland, E., Etchegoyhen, K., Amestoy, A., Bouvard, M., & Sauzéon, H. (2018). Tablet apps to support first school inclusion of children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in mainstream classrooms: A pilot study. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02020
Fleury, V. P., Hedges, S., Hume, K., Browder, D. M., Thompson, J. L., Fallin, K., El Zein, F., Reutebuch, C. K., & Vaughn, S. (2014). Addressing the academic needs of adolescents with autism spectrum disorder in secondary education. Remedial and Special Education, 35(2), 68-79. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932513518823
Gilal, N. G., Zhang, J., & Gilal, F. G. (2018). The four-factor model of product design: scale development and validation. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 27(6), 684-700. https://doi.org/10.1108/jpbm-11-2017-1659
Gelbar, N. W., Anderson, C., Mccarthy, S., & Buggey, T. (2012). Video self-modeling as an intervention strategy for individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Psychology in the Schools, 49(1), 15-22. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.20628
Gevarter, C., Bryant, D. P., Bryant, B., Watkins, L., Zamora, C., & Sammarco, N. (2016). Mathematics interventions for individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Review Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 3, 224-238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40489-016-0078-9
Hewagamage, K. P., Nishakumari, K. M. G. B., & Wikramanayake, G. (2011). Developing online virtual community by facilitating student discussions. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 1(4), 303-308. https://doi.org/10.7763/ijiet.2011.v1.49
Itskovich, E., Zyga, O., Libove, R. A., Phillips, J. M., Garner, J. P., & Parker, K. J. (2021). Complex interplay between cognitive ability and social motivation in predicting social skill: A unique role for social motivation in children with autism. Autism Research, 14(1), 86-92. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2409
King, S. A., Lemons, C. J., & Davidson, K. A. (2016). Math interventions for students with autism spectrum disorder: A best-evidence synthesis. Exceptional Children, 82(4) 443-462. https://doi.org/10.1177/0014402915625066
Koegel, R. L., Koegel, L. K., Vernon, T. W., & Brookman-Frazee, L. I. (2010). Empirically supported pivotal response treatment for children with autism spectrum disorders. In J. R. Weisz & A.E. Kazdin (Eds.), Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (2nd ed., pp. 327-344). The Guilford Press.
Koller, H. P. (2012). Visual processing and learning disorders. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology, 25(2), 377-383. https://doi.org/10.1097/ICU.0b013e32835720e2
Mayer, R. E., & Sims, V. K. (1994). For whom is a picture worth a thousand words? Extensions of a dual-coding theory of multimedia learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 86(3), 389-401. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.86.3.389
McMahon, J., & Cullinan, V. (2014). Education programmes for young children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An evaluation framework. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 35(12), 3689-3697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.09.004
Miller, N., Wyatt, J., Casey, L. B., & Smith, J. B. (2018). Using computer-assisted instruction to increase the eye gaze of children with autism. Behavioral Interventions, 33(1), 3-12. https://doi.org/10.1002/bin.1507
Moore, D., McGrath, P., & Thorpe, J. (2000). Computer-aided learning for people with autism - A framework for research and development. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 37(3), 218-228. https://doi.org/10.1080/13558000050138452
Moore, M., & Calvert, S. (2000). Brief report: Vocabulary acquisition for children with autism: Teacher or computer instruction. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 359-362 https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005535602064
Najdowski, A. C., Gould, E. R., Lanagan, T. M., & Bishop, M. R. (2014). Designing curriculum programs for children with autism. In J. Tarbox, D. R. Dixon, P. Sturmey, & J. L. Matson (Eds.), Handbook of early intervention for autism spectrum disorders (pp. 179-204). Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0401-3_10
Odom, S. L., Collet-Klingenberg, L., Rogers, S. J., & Hatton, D. D. (2010). Evidence-based practices in interventions for children and youth with autism spectrum disorders. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 54(4), 275-282. https://doi.org/10.1080/10459881003785506
Park, M. N., Moulton, E. E., & Laugeson, E. A. (2023). Parent-assisted social skills training for children with autism spectrum disorder: PEERS for preschoolers. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 38(2), 80-89. https://doi.org/10.1177/10883576221110158
Parsons, S., & Cobb, S. (2011). State-of-the-art of virtual reality technologies for children on the autism spectrum. European Journal of Special Needs Education, 26(3), 355-366. https://doi.org/10.1080/08856257.2011.593831
Pennington, R. C. (2010). Computer-assisted instruction for teaching academic skills to students with autism spectrum disorders: A review of literature. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 25(4), 239-248. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088357610378291
Pertiwi, L. K., & Djoehaeni, H. (2021, March). Analysis of early childhood tutorial content to improve reading, writing, and arithmetic skills [Paper presentation]. In Advances in social science, education and humanities research. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Early Childhood Education (ICECE 2020) (pp. 130-135). Atlantis Press. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.210322.028
Plass, J. L., Chun, D. M., Mayer, R. E., & Leutner, D. (1998). Supporting visual and verbal learning preferences in a second-language multimedia learning environment. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(1), 25-36. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.90.1.25
Ramdoss, S., MacHalicek, W., Rispoli, M., Mulloy, A., Lang, R., & O’Reilly, M. (2012). Computer-based interventions to improve social and emotional skills in individuals with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Developmental Neurorehabilitation, 15(2), 119-135. https://doi.org/10.3109/17518423.2011.651655
Ramli, J. A., & Surbaini, K. N. (2023). Assessing personal attributes and virtual learning engagement during pandemic among accounting undergraduates. In A. H. Jaaffar, S. Buniamin, N. R. A. Rahman, N. S. Othman, N. Mohammad, S. Kasavan, N. E. A. B. Mohamad, Z. M. Saad, F. A. Ghani, & N. I. N. Redzuan (Eds.), Accelerating Transformation towards Sustainable and Resilient Business: Lessons Learned from the COVID-19 Crisis, vol 1. European Proceedings of Finance and Economics (pp. 982-990). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epfe.23081.91
Ring, E., & Prunty, A. (2012). Adapting the curriculum to include learners with autistic spectrum disorders in Irish schools. In Special and Inclusive Education: A Research Perspective (Vol. 9783034308762, pp. 289-302). Peter Lang Publishing Group.
Sansosti, F. J., & Powell-Smith, K. A. (2008). Using computer-presented social stories and video models to increase the social communication skills of children with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 10(3), 162-178. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300708316259
Shin, M., Park, J., Grimes, R., & Bryant, D. P. (2021). Effects of using virtual manipulatives for students with disabilities: Three-level multilevel modeling for single-case data. Exceptional Children, 87(4), 418-437. https://doi.org/10.1177/00144029211007150
Strickland, D. (1996). A virtual reality application with autistic children. Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, 5(3), 319-329. https://doi.org/10.1162/pres.1996.5.3.319
Subandi, I. P. and Hidayah, R. (2023). Validity of electronic student worksheets to improve students' metacognitive skills through pbl on petroleum materials. Hydrogen: Jurnal Kependidikan Kimia, 11(4), 391-400. https://doi.org/10.33394/hjkk.v11i4.8236
Tuedor, M., Franco, F., White, A., Smith, S., & Adams, R. (2019). Testing literacy educational software to develop design guidelines for children with autism. International Journal of Disability, Development and Education, 66(1), 19-35. https://doi.org/10.1080/1034912X.2018.1450494
Viljaranta, J., Lerkkanen, M. K., Poikkeus, A. M., Aunola, K., & Nurmi, J. E. (2009). Cross-lagged relations between task motivation and performance in arithmetic and literacy in kindergarten. Learning and Instruction, 19(4), 335-344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.06.011