Main Article Content
Abstract
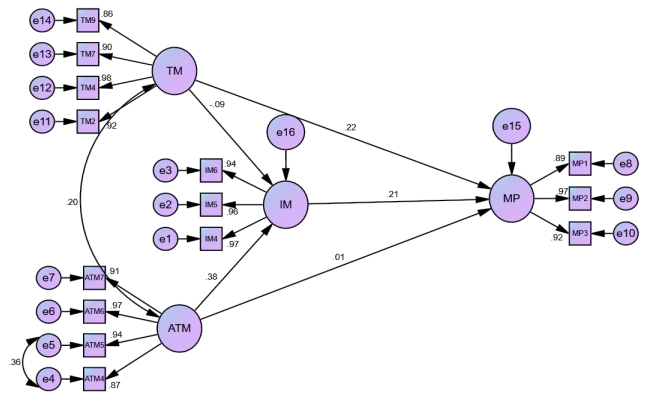
This research work surveyed inquired into, and scanned carefully, the exhibiting indirect causation of learners’ mathematics perception, a connection jointly engaging learners’ stance towards mathematics and technology on their mathematics interest. This inquest was conducted on 200 Senior High School learners sampled in the Central part of Ghana. The employment of a survey and comprehensive questionnaire was necessitated. Amos Software (v. 23) was instrumental in the Modeling analysis computations (SEM: EFA/CFA), and the paths were tested on the hypotheses. Attitude towards mathematics produced a positive impact on learners’ interest, which in turn impacted positively on learners’ perception of mathematics, and technology yielded a positive impact on how learners perceive mathematics. There was a complete mediation of learners' perception of mathematics in the association between learners' attitudes towards mathematics and their interest in mathematics. Further studies could be carried out on the parameters using other methods to inquire about the impact of learners' attitudes on mathematics and the technology involved in their learning on their mathematics interests. The education system must be mindful of learners' attitudes, perceptions, and technology in their learning process. Colleges of education must bring up teachers in the light of learners' attitudes, perceptions, and technology in their learning and the appropriate pedagogy in their delivery of lessons.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2023 Peter Yeribatuah, Yarhands Dissou Arthur

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Adams, A. M., Wilson, H., Money, J., Palmer-Conn, S., & Fearn, J. (2020). Student engagement with feedback and attainment: the role of academic self-efficacy. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education, 45(2), 317–329. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2019.1640184
- Alam, A. (2020). Challenges and possibilities in teaching and learning of calculus: A case study of India. Journal for the Education of Gifted Young Scientists, 8(1), 407–433. https://doi.org/10.17478/jegys.660201
- Amoako, T., Sheng, Z. H., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Pomegbe, W. W. K. (2022). Assessing the Moderation Role of ICT in the Relationship between Supply Chain Integration and SME Performance. Journal of Industrial Integration and Management, 7(2), 203–233. https://doi.org/10.1142/S2424862221500160
- Arhin, D., & Gideon, E. (2020). Relationship between Students ’ Interest and Academic Performance in Mathematics : A Study of Agogo State College. Global Scientific Journals, 8(6), 389–396.
- Arthur, Y., Addo, S., & Annan, J. (2015). Student Mathematics Interest in Ghana: The Role of Parent Interest, Gender, Basic School Attended and Fear of Basic School Mathematics Teacher. Advances in Research, 5(5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.9734/air/2015/19889
- Arthur, Y., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Assuah, C. (2017). Students’ Perception and Its Impact on Ghanaian Students’ Interest in Mathematics: Multivariate Statistical Analytical Approach. Asian Research Journal of Mathematics, 4(2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.9734/arjom/2017/33023
- Arthur, Y. D., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Asiedu-Addo, S. K. (2022). Enhancing Performance in Mathematics Through Motivation, Peer Assisted Learning, And Teaching Quality: The Mediating Role of Student Interest. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(2). https://doi.org/10.29333/EJMSTE/11509
- Arthur, Y. D., Owusu, E. K., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Arhin, A. K. (2018). Connecting Mathematics To Real-Life Problems: A Teaching Quality That Improves Students’ Mathematics Interest. IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education, 8(4), 65–71. https://doi.org/10.9790/7388- 0804026571
- Ashton, A. S. (2018). How human resources management best practice influence employee satisfaction and job retention in the Thai hotel industry. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality and Tourism, 17(2), 175–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332845.2017.1340759
- Ayotola, A., & Adedeji, T. (2009). The relationship between mathematics self-efficacy and achievement in mathematics. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 1(1), 953–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2009.01.169
- Azmidar, A., Darhim, D., & Dahlan, J. A. (2017). Enhancing Students’ Interest through Mathematics Learning. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 895(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742- 6596/895/1/012072
- Baah-Duodu, S., Borbye, S., Someah-Addae, E., Ennin, F. C., & Osei-Buabeng, V. (2021). Developing Female Pre-Service Teachers’ Mathematics Self-Efficacy by Integrating History of Mathematics into Teaching During Lesson Study. Social Education Research, 3(1), 91–102. https://doi.org/10.37256/ser.3120221011
- Berger, N., Mackenzie, E., & Holmes, K. (2020). Positive attitudes towards mathematics and science are mutually beneficial for student achievement: a latent profile analysis of TIMSS 2015. In Australian Educational Researcher (Vol. 47, Issue 3). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13384-020-00379-8
- Cai, S., Liu, E., Yang, Y., & Liang, J. C. (2019). Tablet-based AR technology: Impacts on students’ conceptions and approaches to learning mathematics according to their self-efficacy. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(1), 248–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12718
- Callaman, R. A., & Itaas, E. C. (2020). Students’ mathematics achievement in Mindanao context: A meta-analysis. JRAMathEdu (Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education), 5(2), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v5i2.10282
- Casinillo, L. F., Palen, M. A. E., Casinillo, E. L., & Batidor, P. G. (2020). Assessing Senior High Student’s Learning Experiences in Mathematics. Indonesian Journal of Educational Studies, 23(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.26858/ijes.v23i1.13437
- Cetin-Dindar, A. (2016). Student motivation in constructivist learning environment. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 12(2), 233–247. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2016.1399a
- Çevik, M. (2018). Proje Tabanli (PjT) Fen, Teknoloji, Mühendislik ve Matematik (STEM) egitiminin, meslek lisesi ögrencilerinin akademik basarilarina ve mesleki ilgilerine etkisi. Pegem Egitim ve Ogretim Dergisi, 8(2), 281–306. https://doi.org/10.14527/pegegog.2018.012
- Chand, S., Chaudhary, K., Prasad, A., & Chand, V. (2021). Perceived Causes of Students’ Poor Performance in Mathematics: A Case Study at Ba and Tavua Secondary Schools. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 7(April), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fams.2021.614408
- Chu, H. C., Chen, J. M., & Tsai, C. L. (2017). Effects of an online formative peer-tutoring approach on students’ learning behaviors, performance and cognitive load in mathematics. Interactive Learning Environments, 25(2), 203–219. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2016.1276085
- Cochrane, T., & Bateman, R. (2009). Smartphones give you wings: Pedagogical affordances of mobile web 2.0. ASCILITE 2009 - The Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education, 26(1), 142–152.
- Cordero, J. M., & Gil-Izquierdo, M. (2018). The effect of teaching strategies on student achievement: An analysis using TALIS-PISA-link. Journal of Policy Modeling, 40(6), 1313–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2018.04.003
- Das, K. (2020). Realistic Mathematics & Vygotsky’s Theories in Mathematics Education. Shanlax International Journal of Education, 9(1), 104–108. https://doi.org/10.34293/education.v9i1.3346
- dos Santos, P. M., & Cirillo, M. Â. (2021). Construction of the average variance extracted index for construct validation in structural equation models with adaptive regressions. Communications in Statistics: Simulation and Computation, 0(0), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610918.2021.1888122
- Eyyam, R., & Yaratan, H. S. (2014). Impact of Use of Technology in Mathematics Lessons on Student Achievement and Attitudes. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 42(1), 31S-42S. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2014.42.0.s31
- Faber, J. M., Luyten, H., & Visscher, A. J. (2017). The effects of a digital formative assessment tool on mathematics achievement and student motivation: Results of a randomized experiment. Computers and Education, 106, 83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.12.001
- Fabian, K., Topping, K. J., & Barron, I. G. (2018a). Using mobile technologies for mathematics: effects on student attitudes and achievement. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1119–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9580-3
- Fabian, K., Topping, K. J., & Barron, I. G. (2018b). Using mobile technologies for mathematics: effects on student attitudes and achievement. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1119–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9580-3
- Fried, M. N. (2001). Can mathematics education and history of mathematics coexist? Science and Education, 10(4), 391–408. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011205014608
- Fung, F., Tan, C. Y., & Chen, G. (2018). Student engagement and mathematics achievement: Unraveling main and interactive effects. Psychology in the Schools, 55(7), 815–831. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22139
- Gokkurt, B., Dundar, S., Soylu, Y., & Akgun, L. (2012). The Effects of Learning Together Technique Which is based on Cooperative Learning on Students’ Achieevement in Mathematics Class. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 46, 3431–3434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.079
- Gómez-García, M., Hossein-Mohand, H., Trujillo-Torres, J. M., Hossein-Mohand, H., & Aznar-Díaz, I. (2020). Technological factors that influence the mathematics performance of secondary school students. Mathematics, 8(11), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8111935
- Habók, A., Magyar, A., Németh, M. B., & Csapó, B. (2020). Motivation and self-related beliefs as predictors of academic achievement in reading and mathematics: Structural equation models of longitudinal data. International Journal of Educational Research, 103(February), 101634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101634
- Heck, R. H., & Mahoe, R. (2010). Student course taking and teacher quality: Their effects on achievement and growth. International Journal of Educational Management, 24(1), 56–72. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513541011013051
- Higgins, K., Huscroft-D’Angelo, J., & Crawford, L. (2019). Effects of Technology in Mathematics on Achievement, Motivation, and Attitude: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57(2), 283–319. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633117748416
- Hillmayr, D., Ziernwald, L., Reinhold, F., Hofer, S. I., & Reiss, K. M. (2020). The potential of digital tools to enhance mathematics and science learning in secondary schools: A context-specific meta- analysis. Computers and Education, 153(April), 103897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103897
- Huang, M. C. L., Chou, C. Y., Wu, Y. T., Shih, J. L., Yeh, C. Y. C., Lao, A. C. C., Fong, H., Lin, Y. F., & Chan, T. W. (2020). Interest-driven video creation for learning mathematics. In Journal of Computers in Education (Vol. 7, Issue 3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-020-00161-w Jankvist, U. T., Clark, K. M., & Mosvold, R. (2020). Developing mathematical knowledge for teaching teachers: potentials of history of mathematics in teacher educator training. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 23(3), 311–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-018-09424-x
- Karatas-Aydin, F. I., & Isiksal-Bostan, M. (2022). Through Their Eyes: Gifted Students’ Views on Integrating History of Mathematics Embedded Videos Into Mathematics Classrooms. SAGE Open, 12(2), 215824402210995. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221099518
- Kosel, C., Wolter, I., & Seidel, T. (2021). Profiling secondary school students in mathematics and German language arts using learning-relevant cognitive and motivational-affective characteristics. Learning and Instruction, 73(October 2020), 101434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2020.101434
- Kusumawati, I. B., Fachrudin, A. D., Kohar, A. W., & Widadah, S. (2020). History of Mathematics for Teaching Mathematics: The Case of Indonesian Prospective Teachers’ Beliefs and Attitudes. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(6), 2305–2314. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.080614
- Leyva, E., Walkington, C., Perera, H., & Bernacki, M. (2022). Making Mathematics Relevant: an Examination of Student Interest in Mathematics, Interest in STEM Careers, and Perceived Relevance. International Journal of Research in Undergraduate Mathematics Education, 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40753-021-00159-4
- Li, L., Peng, Z., Lu, L., Liao, H., & Li, H. (2020). Peer relationships, self-efficacy, academic motivation, and mathematics achievement in Zhuang adolescents: A moderated mediation model. Children and Youth Services Review, 118(August), 105358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105358
- Marsh, H. W., Guo, J., Dicke, T., Parker, P. D., & Craven, R. G. (2020). Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA), Exploratory Structural Equation Modeling (ESEM), and Set-ESEM: Optimal Balance Between Goodness of Fit and Parsimony. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 55(1), 102–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2019.1602503
- Mazana, M. Y., Montero, C. S., & Casmir, R. O. (2018). Investigating Students’ Attitude towards Learning Mathematics. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(1), 207–231. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/3997
- Mishra, M., Gorakhnath, I., Lata, P., Rani, R., & Chopra, P. (2022). Integration of technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) in classrooms through a teacher’s lens. International Journal of Health Sciences, 6(June), 12505–12512. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6ns3.9536
- Monrat, N., Phaksunchai, M., & Chonchaiya, R. (2022). Developing Students’ Mathematical Critical Thinking Skills Using Open-Ended Questions and Activities Based on Student Learning Preferences. Education Research International, 2022(2015). hhttps://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3300363
- Otoo, D., Iddrisu, W. A., Kessie, J. A., & Larbi, E. (2018). Structural Model of Students’ Interest and Self-Motivation to Learning Mathematics. Education Research International, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9417109
- Partovi, T., & Razavi, M. R. (2019). The effect of game-based learning on academic achievement motivation of elementary school students. Learning and Motivation, 68(June), 101592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lmot.2019.101592
- Parveen, Q., Mahmood, S. T, Mahmood, A., & Arif, M. (2011). Effect of cooperative learning on academic achievement of 8 th grade students in the subject of social studies. International Journal of Academic Research, 3(1), 950-954.
- Ran, H., Kim, N. J., & Secada, W. G. (2022). A meta-analysis on the effects of technology’s functions and roles on students’ mathematics achievement in K-12 classrooms. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 38(1), 258–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12611
- Şahin, Ö., & Danaci, D. (2020). Investigating the effect of history-of-mathematics activities on middle- grade students’ mental computation and opinions: an action research. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1857859
- Samuel, T. S., & Warner, J. (2021). “I Can Math!”: Reducing Math Anxiety and Increasing Math Self- Efficacy Using a Mindfulness and Growth Mindset-Based Intervention in First-Year Students. Community College Journal of Research and Practice, 45(3), 205–222. https://doi.org/10.1080/10668926.2019.1666063
- Shara, J. (2020). Benefits from Integrating History of Mathematics into Teaching. October, 1–10. http://users.sch.gr/afylakis/ME2013/ME2013JShara.pdf
- Singh, K., Granville, M., & Dika, S. (2002). Mathematics and science achievement: Effects of motivation, interest, and academic engagement. Journal of Educational Research, 95(6), 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220670209596607
- Tambunan, H. (2019). The Effectiveness of the Problem Solving Strategy and the Scientific Approach to Students ’ Mathematical Capabilities in High Order Thinking Skills. 14(2), 293–302.
- Tambunan, H., Sinaga, B., & Widada, W. (2021). Analysis of teacher performance to build student interest and motivation towards mathematics achievement. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 10(1), 42–47. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v10i1.20711
- Vaiopoulou, J., Papadakis, S., Sifaki, E., Stamovlasis, D., & Kalogiannakis, M. (2021). Parents’ perceptions of educational apps use for kindergarten children: Development and validation of a new instrument (peau-p) and exploration of parents’ profiles. Behavioral Sciences, 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11060082
- Yalçin, K., & Hasan, A. (2018). The effect of cooperative learning on the academic achievement and attitude of students in Mathematics class. Educational Research and Reviews, 13(21), 712–722. https://doi.org/10.5897/err2018.3636
- Yeh, C. Y. C., Cheng, H. N. H., Chen, Z. H., Liao, C. C. Y., & Chan, T. W. (2019). Enhancing achievement and interest in mathematics learning through Math-Island. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-019-0100-9
References
Adams, A. M., Wilson, H., Money, J., Palmer-Conn, S., & Fearn, J. (2020). Student engagement with feedback and attainment: the role of academic self-efficacy. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education, 45(2), 317–329. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2019.1640184
Alam, A. (2020). Challenges and possibilities in teaching and learning of calculus: A case study of India. Journal for the Education of Gifted Young Scientists, 8(1), 407–433. https://doi.org/10.17478/jegys.660201
Amoako, T., Sheng, Z. H., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Pomegbe, W. W. K. (2022). Assessing the Moderation Role of ICT in the Relationship between Supply Chain Integration and SME Performance. Journal of Industrial Integration and Management, 7(2), 203–233. https://doi.org/10.1142/S2424862221500160
Arhin, D., & Gideon, E. (2020). Relationship between Students ’ Interest and Academic Performance in Mathematics : A Study of Agogo State College. Global Scientific Journals, 8(6), 389–396.
Arthur, Y., Addo, S., & Annan, J. (2015). Student Mathematics Interest in Ghana: The Role of Parent Interest, Gender, Basic School Attended and Fear of Basic School Mathematics Teacher. Advances in Research, 5(5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.9734/air/2015/19889
Arthur, Y., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Assuah, C. (2017). Students’ Perception and Its Impact on Ghanaian Students’ Interest in Mathematics: Multivariate Statistical Analytical Approach. Asian Research Journal of Mathematics, 4(2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.9734/arjom/2017/33023
Arthur, Y. D., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Asiedu-Addo, S. K. (2022). Enhancing Performance in Mathematics Through Motivation, Peer Assisted Learning, And Teaching Quality: The Mediating Role of Student Interest. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(2). https://doi.org/10.29333/EJMSTE/11509
Arthur, Y. D., Owusu, E. K., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Arhin, A. K. (2018). Connecting Mathematics To Real-Life Problems: A Teaching Quality That Improves Students’ Mathematics Interest. IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education, 8(4), 65–71. https://doi.org/10.9790/7388- 0804026571
Ashton, A. S. (2018). How human resources management best practice influence employee satisfaction and job retention in the Thai hotel industry. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality and Tourism, 17(2), 175–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332845.2017.1340759
Ayotola, A., & Adedeji, T. (2009). The relationship between mathematics self-efficacy and achievement in mathematics. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 1(1), 953–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2009.01.169
Azmidar, A., Darhim, D., & Dahlan, J. A. (2017). Enhancing Students’ Interest through Mathematics Learning. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 895(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742- 6596/895/1/012072
Baah-Duodu, S., Borbye, S., Someah-Addae, E., Ennin, F. C., & Osei-Buabeng, V. (2021). Developing Female Pre-Service Teachers’ Mathematics Self-Efficacy by Integrating History of Mathematics into Teaching During Lesson Study. Social Education Research, 3(1), 91–102. https://doi.org/10.37256/ser.3120221011
Berger, N., Mackenzie, E., & Holmes, K. (2020). Positive attitudes towards mathematics and science are mutually beneficial for student achievement: a latent profile analysis of TIMSS 2015. In Australian Educational Researcher (Vol. 47, Issue 3). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13384-020-00379-8
Cai, S., Liu, E., Yang, Y., & Liang, J. C. (2019). Tablet-based AR technology: Impacts on students’ conceptions and approaches to learning mathematics according to their self-efficacy. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(1), 248–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12718
Callaman, R. A., & Itaas, E. C. (2020). Students’ mathematics achievement in Mindanao context: A meta-analysis. JRAMathEdu (Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education), 5(2), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v5i2.10282
Casinillo, L. F., Palen, M. A. E., Casinillo, E. L., & Batidor, P. G. (2020). Assessing Senior High Student’s Learning Experiences in Mathematics. Indonesian Journal of Educational Studies, 23(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.26858/ijes.v23i1.13437
Cetin-Dindar, A. (2016). Student motivation in constructivist learning environment. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 12(2), 233–247. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2016.1399a
Çevik, M. (2018). Proje Tabanli (PjT) Fen, Teknoloji, Mühendislik ve Matematik (STEM) egitiminin, meslek lisesi ögrencilerinin akademik basarilarina ve mesleki ilgilerine etkisi. Pegem Egitim ve Ogretim Dergisi, 8(2), 281–306. https://doi.org/10.14527/pegegog.2018.012
Chand, S., Chaudhary, K., Prasad, A., & Chand, V. (2021). Perceived Causes of Students’ Poor Performance in Mathematics: A Case Study at Ba and Tavua Secondary Schools. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 7(April), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fams.2021.614408
Chu, H. C., Chen, J. M., & Tsai, C. L. (2017). Effects of an online formative peer-tutoring approach on students’ learning behaviors, performance and cognitive load in mathematics. Interactive Learning Environments, 25(2), 203–219. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2016.1276085
Cochrane, T., & Bateman, R. (2009). Smartphones give you wings: Pedagogical affordances of mobile web 2.0. ASCILITE 2009 - The Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education, 26(1), 142–152.
Cordero, J. M., & Gil-Izquierdo, M. (2018). The effect of teaching strategies on student achievement: An analysis using TALIS-PISA-link. Journal of Policy Modeling, 40(6), 1313–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2018.04.003
Das, K. (2020). Realistic Mathematics & Vygotsky’s Theories in Mathematics Education. Shanlax International Journal of Education, 9(1), 104–108. https://doi.org/10.34293/education.v9i1.3346
dos Santos, P. M., & Cirillo, M. Â. (2021). Construction of the average variance extracted index for construct validation in structural equation models with adaptive regressions. Communications in Statistics: Simulation and Computation, 0(0), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610918.2021.1888122
Eyyam, R., & Yaratan, H. S. (2014). Impact of Use of Technology in Mathematics Lessons on Student Achievement and Attitudes. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 42(1), 31S-42S. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2014.42.0.s31
Faber, J. M., Luyten, H., & Visscher, A. J. (2017). The effects of a digital formative assessment tool on mathematics achievement and student motivation: Results of a randomized experiment. Computers and Education, 106, 83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.12.001
Fabian, K., Topping, K. J., & Barron, I. G. (2018a). Using mobile technologies for mathematics: effects on student attitudes and achievement. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1119–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9580-3
Fabian, K., Topping, K. J., & Barron, I. G. (2018b). Using mobile technologies for mathematics: effects on student attitudes and achievement. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1119–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9580-3
Fried, M. N. (2001). Can mathematics education and history of mathematics coexist? Science and Education, 10(4), 391–408. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011205014608
Fung, F., Tan, C. Y., & Chen, G. (2018). Student engagement and mathematics achievement: Unraveling main and interactive effects. Psychology in the Schools, 55(7), 815–831. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22139
Gokkurt, B., Dundar, S., Soylu, Y., & Akgun, L. (2012). The Effects of Learning Together Technique Which is based on Cooperative Learning on Students’ Achieevement in Mathematics Class. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 46, 3431–3434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.079
Gómez-García, M., Hossein-Mohand, H., Trujillo-Torres, J. M., Hossein-Mohand, H., & Aznar-Díaz, I. (2020). Technological factors that influence the mathematics performance of secondary school students. Mathematics, 8(11), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8111935
Habók, A., Magyar, A., Németh, M. B., & Csapó, B. (2020). Motivation and self-related beliefs as predictors of academic achievement in reading and mathematics: Structural equation models of longitudinal data. International Journal of Educational Research, 103(February), 101634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101634
Heck, R. H., & Mahoe, R. (2010). Student course taking and teacher quality: Their effects on achievement and growth. International Journal of Educational Management, 24(1), 56–72. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513541011013051
Higgins, K., Huscroft-D’Angelo, J., & Crawford, L. (2019). Effects of Technology in Mathematics on Achievement, Motivation, and Attitude: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57(2), 283–319. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633117748416
Hillmayr, D., Ziernwald, L., Reinhold, F., Hofer, S. I., & Reiss, K. M. (2020). The potential of digital tools to enhance mathematics and science learning in secondary schools: A context-specific meta- analysis. Computers and Education, 153(April), 103897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103897
Huang, M. C. L., Chou, C. Y., Wu, Y. T., Shih, J. L., Yeh, C. Y. C., Lao, A. C. C., Fong, H., Lin, Y. F., & Chan, T. W. (2020). Interest-driven video creation for learning mathematics. In Journal of Computers in Education (Vol. 7, Issue 3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-020-00161-w Jankvist, U. T., Clark, K. M., & Mosvold, R. (2020). Developing mathematical knowledge for teaching teachers: potentials of history of mathematics in teacher educator training. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 23(3), 311–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-018-09424-x
Karatas-Aydin, F. I., & Isiksal-Bostan, M. (2022). Through Their Eyes: Gifted Students’ Views on Integrating History of Mathematics Embedded Videos Into Mathematics Classrooms. SAGE Open, 12(2), 215824402210995. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221099518
Kosel, C., Wolter, I., & Seidel, T. (2021). Profiling secondary school students in mathematics and German language arts using learning-relevant cognitive and motivational-affective characteristics. Learning and Instruction, 73(October 2020), 101434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2020.101434
Kusumawati, I. B., Fachrudin, A. D., Kohar, A. W., & Widadah, S. (2020). History of Mathematics for Teaching Mathematics: The Case of Indonesian Prospective Teachers’ Beliefs and Attitudes. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(6), 2305–2314. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.080614
Leyva, E., Walkington, C., Perera, H., & Bernacki, M. (2022). Making Mathematics Relevant: an Examination of Student Interest in Mathematics, Interest in STEM Careers, and Perceived Relevance. International Journal of Research in Undergraduate Mathematics Education, 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40753-021-00159-4
Li, L., Peng, Z., Lu, L., Liao, H., & Li, H. (2020). Peer relationships, self-efficacy, academic motivation, and mathematics achievement in Zhuang adolescents: A moderated mediation model. Children and Youth Services Review, 118(August), 105358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105358
Marsh, H. W., Guo, J., Dicke, T., Parker, P. D., & Craven, R. G. (2020). Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA), Exploratory Structural Equation Modeling (ESEM), and Set-ESEM: Optimal Balance Between Goodness of Fit and Parsimony. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 55(1), 102–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2019.1602503
Mazana, M. Y., Montero, C. S., & Casmir, R. O. (2018). Investigating Students’ Attitude towards Learning Mathematics. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(1), 207–231. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/3997
Mishra, M., Gorakhnath, I., Lata, P., Rani, R., & Chopra, P. (2022). Integration of technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) in classrooms through a teacher’s lens. International Journal of Health Sciences, 6(June), 12505–12512. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6ns3.9536
Monrat, N., Phaksunchai, M., & Chonchaiya, R. (2022). Developing Students’ Mathematical Critical Thinking Skills Using Open-Ended Questions and Activities Based on Student Learning Preferences. Education Research International, 2022(2015). hhttps://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3300363
Otoo, D., Iddrisu, W. A., Kessie, J. A., & Larbi, E. (2018). Structural Model of Students’ Interest and Self-Motivation to Learning Mathematics. Education Research International, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9417109
Partovi, T., & Razavi, M. R. (2019). The effect of game-based learning on academic achievement motivation of elementary school students. Learning and Motivation, 68(June), 101592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lmot.2019.101592
Parveen, Q., Mahmood, S. T, Mahmood, A., & Arif, M. (2011). Effect of cooperative learning on academic achievement of 8 th grade students in the subject of social studies. International Journal of Academic Research, 3(1), 950-954.
Ran, H., Kim, N. J., & Secada, W. G. (2022). A meta-analysis on the effects of technology’s functions and roles on students’ mathematics achievement in K-12 classrooms. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 38(1), 258–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12611
Şahin, Ö., & Danaci, D. (2020). Investigating the effect of history-of-mathematics activities on middle- grade students’ mental computation and opinions: an action research. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1857859
Samuel, T. S., & Warner, J. (2021). “I Can Math!”: Reducing Math Anxiety and Increasing Math Self- Efficacy Using a Mindfulness and Growth Mindset-Based Intervention in First-Year Students. Community College Journal of Research and Practice, 45(3), 205–222. https://doi.org/10.1080/10668926.2019.1666063
Shara, J. (2020). Benefits from Integrating History of Mathematics into Teaching. October, 1–10. http://users.sch.gr/afylakis/ME2013/ME2013JShara.pdf
Singh, K., Granville, M., & Dika, S. (2002). Mathematics and science achievement: Effects of motivation, interest, and academic engagement. Journal of Educational Research, 95(6), 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220670209596607
Tambunan, H. (2019). The Effectiveness of the Problem Solving Strategy and the Scientific Approach to Students ’ Mathematical Capabilities in High Order Thinking Skills. 14(2), 293–302.
Tambunan, H., Sinaga, B., & Widada, W. (2021). Analysis of teacher performance to build student interest and motivation towards mathematics achievement. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 10(1), 42–47. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v10i1.20711
Vaiopoulou, J., Papadakis, S., Sifaki, E., Stamovlasis, D., & Kalogiannakis, M. (2021). Parents’ perceptions of educational apps use for kindergarten children: Development and validation of a new instrument (peau-p) and exploration of parents’ profiles. Behavioral Sciences, 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11060082
Yalçin, K., & Hasan, A. (2018). The effect of cooperative learning on the academic achievement and attitude of students in Mathematics class. Educational Research and Reviews, 13(21), 712–722. https://doi.org/10.5897/err2018.3636
Yeh, C. Y. C., Cheng, H. N. H., Chen, Z. H., Liao, C. C. Y., & Chan, T. W. (2019). Enhancing achievement and interest in mathematics learning through Math-Island. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-019-0100-9