Main Article Content
Abstract
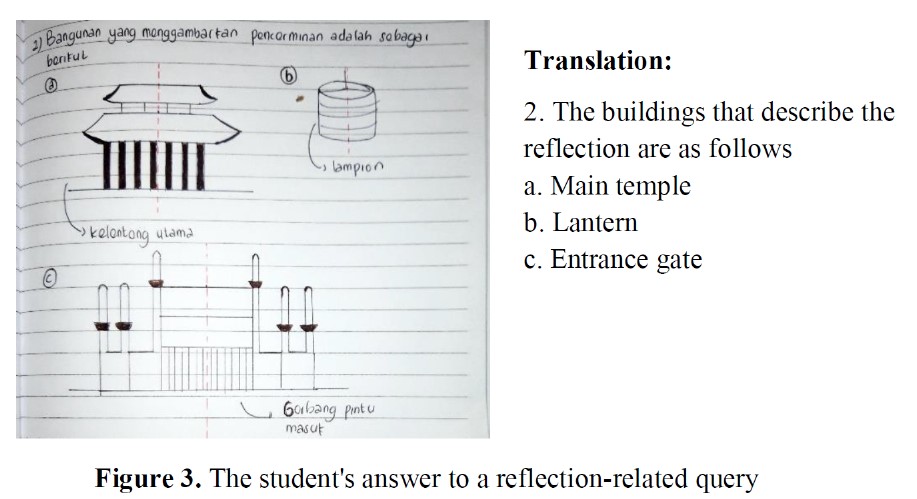
Sam Poo Kong is one of Semarang's city cultural heritages. This historical structure features intriguing architecture as well as being a popular tourist destination. This study aims to explore Sam Poo Kong's building as a starting point in the geometric transformation course. Besides, the study method is descriptive in qualitative terms with the ethnography approach, namely the type of research to describe and acquire data as a whole, comprehensive, and in-depth. The result is an ethnomathematics exploration of Sam Poo Kong's historic buildings, representing mathematical concepts including reflection, translation, rotation, dilation, and cultural values. Based on implementation in transformation class, students can quickly grasp which Sam Poo Kong's building portrays transformation. Students can identify and describe the Sam Poo Kong building's transformation forms, which include: 1) reflection on the temple as a whole, ornaments, and Sam Poo Kong entrance gates; 2) translation on the statues, roofs, lanterns, and poles; 3) rotation on the bedug, reliefs, incense holders, lanterns, and anchors; and 4) dilatation of the inner and outer rooflines of the Sam Poo Kong building. This can stimulate students to envisage the types of transformation, which makes the information easier to learn.Moreover, this study can benefit teachers for local wisdom context reference in geometric transformation and following researchers for further study.
DOI : https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.13073.15-28
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2022 Fifin Aisyah, Aidha Aprilia Puji Lestari, Muhammad Agus Supriyanto, Farida Nursyahidah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Abdullah, A. (2016). Ethnomathematics in Perspective Sundanese Culture. Journal On Mathematics Education, 8(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.8.1.3877.1-15
- Adhigwhinyo, P. K. D., & Handoko, B. (2017). Kajian Arsitektural dan Filosofis Budaya Tionghoa pada Klenteng Jin De Yuan, Jakarta. Jurnal Tingkat Sarjana Bidang Seni Rupa dan Desain.
- Aktaş, G. S., & Ünlü, M. (2017). Understanding of Eight Grade Students about Transformation Geometry: Perspectives on Students' Mistakes. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 5(5), 103-119. https://doi.org/10.11114/jets.v5i5.2254
- Arbowo, B., Lestari, A., Aisyah, F., & Nursyahidah, F. (2018). Developing Students Activity with Wisanggeni Puppet Context to Enhance Students' Understanding of Addition and Subtraction Thousands Number. Proceedings of the Mathematics, Informatics, Science, And Education International Conference (MISEIC 2018), 157, 266-269. Surabaya: Universitas Negeri Surabaya.https://doi.org/10.2991/miseic-18.2018.64
- Ardiyani, S., Gunarhadi, G., & Riyadi, R. (2018). Realistic Mathematics Education in Cooperative Learning Viewed from Learning Activity. Journal on Mathematics Education, 9(2), 301-310. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.5392.301-310
- Burais, Listika, dkk. (2016). Peningkatan Kemampuan Penalaran Matematis Siswa melalui Model Discovery Learning. Jurnal Didaktik Matematika, 3(1).http://jurnal.unsyiah.ac.id/DM/article/view/4639
- Bustang, Zulkardi, Darmowijoyo, dolk, M.,& Van Eerde, D. (2013). Developing a Local Instruction Theory for Learning the Concept of Angle through Visual Field Activities and Spatial Representations. International Education Studies, 6(8), 58-70.https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v6n8p58
- CNN Indonesia. (2018, Oktober 30). Sam Poo Kong Saksi Bisu Penjelaajahan Cheng Ho di Indonesia [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WpGoPltigjY
- Duckworth, E. (2013). Helping students get to where ideas can find them. Journal of the New Educator,5(3), 1-10.https://doi.org/10.1080/1547688X.2009.10399573
- Evidiasari, S.,Subanji,&Irawati, S. 2019. Students' Spatial Reasoning in Solving Geometrical Transformation Problems.Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 1(2), 38-51. https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v1i2.8703
- Fahrurozi et al. (2018). Developing Learning Trajectory Based Instruction of the Congruence for Ninth Grade Using Central Java Historical Building. Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education, 3(2), 78-85.https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v3i2.6616
- Fife, J. H., James, K., & Bauer, M. (2019). A learning progression for geometric transformations. Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service.https://doi.org/10.1002/ets2.12236
- Gay, L. R., Mills, G. E.,& Airasian, P. W.(1996).Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Applications.New Jersey: Pearson Education.
- Guven, B. (2012). Using Dynamic Geometry Software to Improve Eight Grade Students' Understanding of Transformation Geometry. Australian Journal of Educational Technology,28(2), 1-14.https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.878
- Hasibuan et al. (2018). Development of Learning Materials Based on Realistic Mathematics Education to Improve Problem Solving Ability and Student Learning Independence. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education,14(1), 243-252.https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/4000
- Hermawan, B. & Prihatmaji, Y. P. (2019). Perkembangan Bentukan Atap Rumah Tradisional Jawa.
- Prosiding Seminar Nasional Desain dan Arsitektur (SENADA).
- Julianto, E. N. (2015). Spirit Pluralisme dalam Klenteng Sam Poo Kong Semarang. The Messenger, 7(2), 36-41.http://dx.doi.org/10.26623/themessenger.v7i2.302
- Khaliesh, H. (2014). Arsitektur Tradisional Tionghoa: Tinjauan Terhadap Identitas, Karakter Budaya dan Eksistensinya. Langkau Betang, 1(1), 86-99.
- Kusmaryono, I. (2014). The Importance of Mathematical Power in Mathematics Learning. Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics, Science, and Education 2014 (ICMSE 2014). UNNES: 35–40.https://icmseunnes.com/2015/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/7.pdf
- Marcella, B. S. (2014). Bentuk dan Makna Atap Kelenteng Sam Poo Kong Semarang. Jurnal Arsitektur KOMPOSISI, 10(5), 350-359. https://doi.org/10.24002/jars.v10i5.1094
- Morris, T. & Paulsen, R.(2011). Using Tracing Paper to Teach Transformation Geometry. Amesa Vol. 2. Johannesburg: Amesa.
- Naidoo, J. (2010). Strategies Used by Grade 12 Mathematics Learners in Transformation Geometry. Natal: University of Kwazulu.
- Nejad, J. M., Zarghami, E., & Abad, A. S. H. (2016). A Study on the Concepts and Themes of Color and Light in the Exquisite Islamic Architecture. Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences, 8(3), 1077-1096. http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/jfas.v8i3.23
- Nuraida, E. M. & Putri, R. I. (2020). The Context of Archipelago Traditional Cake to Explore Students' Understanding in Integers Division Class VII. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(1).https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.1.7400.91-10
- Nursyahidah, F., Ilma, R., & Somakim. (2013). Supporting First Grade Student's Understanding of Addition up to 20 Using Traditional Game. Journal on Mathematics Education,4(2), 212–223. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.4.2.557.212-223
- Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B. A., Albab, I. U., & Aisyah, F. (2020). Pengembangan Learning Trajectory Based Instruction Materi Kerucut Menggunakan Konteks Megono Gunungan. Mosharafa, JurnalPendidikanMatematika,9(1), 47-58.https://doi.org/10.31980/mosharafa.v9i1.560
- Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B. A., & Rubowo, M. R. (2018). A Secondary Student's Problem Solving Ability in Learning Based on Realistic Mathematics with Ethnomathematics. Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education, 3(1), 13-24. https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v3i1.5607
- Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B.A., & Albab, I.U., (2021a). Desain Pembelajaran Kerucut Berkonteks Tradisi Megono Gunungan. Jurnal Elemen,7(1), 14-27. https://doi.org/10.29408/jel.v7i1.2655
- Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B.A., & Albab, I.U., (2021b). Learning cylinder through the context of Giant Lopis tradition. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,1918. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1918/4/042086
- Prahmana, R. C. I. (2010). Permainan “Tepuk Bergilir” yang berorientasikonstruktivisme dalam pembelajaran. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 4(2),1-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.22342/jpm.4.2.406.
- Puspasari, L., Zulkardi, & Somakim. 2015. Desain Pembelajaran Luas Segi Banyak Menggunakan Tangram Berpetak di Kelas IV. Jurnal Inovasi Pembelajaran,1(2).https://doi.org/10.22219/jinop.v1i2.2566
- Ramlan, A. M., & Hali, F. 2018. Analysis of the Difficulty of Mathematical Education Students in Completing the Geometric Running Problem Based on Van Hiele Theory in Geometry Transformation. Journal of Mathematics Education,3(2), 65-70. https://doi.org/10.31327/jomedu.v3i2.834
- Risdiyanti, I., & Prahmana, R.C.I. (2020). The learning trajectory of number pattern learning using Barathayudha war stories and Uno Stacko. Journal on Mathematics Education,11(1), 157- 166.https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.11.1.10225.157-166
- Wahidin dan Sugiman. (2014). Pengaruh Pendekatan PMRI terhadap Motivasi Berprestasi, Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah, dan Prestasi Belajar. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika,9(1).https://doi.org/10.21831/pg.v9i1.9072
- Yanik, H. B. 2014. Middle-school students' concept images of geometric translations.TheJournal of Mathematical Behavior, 36, 33–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2014.08.001
- Yeh et al. 2019.Enhancing achievement and interest in mathematics learning through Math- Island. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 14(1).https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-019-0100-9
- Yeni, E.M. (2011). Pemanfaatan Benda-Benda Mnipulatif untuk Meningkatkan Pemahaman Konsep Geometri dan Kemampuan Tilikan Ruang Siswa kelas V Sekolah Dasar. Proceedings Simantap 2011. Medan: Indonesian Mathematical Society.
- Zhang, D. (2019). Cultural Symbols in Chinese Architecture. Architecture and Design Review, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.18282/adr.v1i1.556
- Zulkardi & Putri, R. I. (2006). Mendesain Sendiri Soal Kontekstual Matematika. Prosiding dalam Konferensi NasionalMatematika ke 13. Semarang: Universitas Negeri Semarang.
References
Abdullah, A. (2016). Ethnomathematics in Perspective Sundanese Culture. Journal On Mathematics Education, 8(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.8.1.3877.1-15
Adhigwhinyo, P. K. D., & Handoko, B. (2017). Kajian Arsitektural dan Filosofis Budaya Tionghoa pada Klenteng Jin De Yuan, Jakarta. Jurnal Tingkat Sarjana Bidang Seni Rupa dan Desain.
Aktaş, G. S., & Ünlü, M. (2017). Understanding of Eight Grade Students about Transformation Geometry: Perspectives on Students' Mistakes. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 5(5), 103-119. https://doi.org/10.11114/jets.v5i5.2254
Arbowo, B., Lestari, A., Aisyah, F., & Nursyahidah, F. (2018). Developing Students Activity with Wisanggeni Puppet Context to Enhance Students' Understanding of Addition and Subtraction Thousands Number. Proceedings of the Mathematics, Informatics, Science, And Education International Conference (MISEIC 2018), 157, 266-269. Surabaya: Universitas Negeri Surabaya.https://doi.org/10.2991/miseic-18.2018.64
Ardiyani, S., Gunarhadi, G., & Riyadi, R. (2018). Realistic Mathematics Education in Cooperative Learning Viewed from Learning Activity. Journal on Mathematics Education, 9(2), 301-310. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.5392.301-310
Burais, Listika, dkk. (2016). Peningkatan Kemampuan Penalaran Matematis Siswa melalui Model Discovery Learning. Jurnal Didaktik Matematika, 3(1).http://jurnal.unsyiah.ac.id/DM/article/view/4639
Bustang, Zulkardi, Darmowijoyo, dolk, M.,& Van Eerde, D. (2013). Developing a Local Instruction Theory for Learning the Concept of Angle through Visual Field Activities and Spatial Representations. International Education Studies, 6(8), 58-70.https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v6n8p58
CNN Indonesia. (2018, Oktober 30). Sam Poo Kong Saksi Bisu Penjelaajahan Cheng Ho di Indonesia [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WpGoPltigjY
Duckworth, E. (2013). Helping students get to where ideas can find them. Journal of the New Educator,5(3), 1-10.https://doi.org/10.1080/1547688X.2009.10399573
Evidiasari, S.,Subanji,&Irawati, S. 2019. Students' Spatial Reasoning in Solving Geometrical Transformation Problems.Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 1(2), 38-51. https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v1i2.8703
Fahrurozi et al. (2018). Developing Learning Trajectory Based Instruction of the Congruence for Ninth Grade Using Central Java Historical Building. Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education, 3(2), 78-85.https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v3i2.6616
Fife, J. H., James, K., & Bauer, M. (2019). A learning progression for geometric transformations. Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service.https://doi.org/10.1002/ets2.12236
Gay, L. R., Mills, G. E.,& Airasian, P. W.(1996).Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Applications.New Jersey: Pearson Education.
Guven, B. (2012). Using Dynamic Geometry Software to Improve Eight Grade Students' Understanding of Transformation Geometry. Australian Journal of Educational Technology,28(2), 1-14.https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.878
Hasibuan et al. (2018). Development of Learning Materials Based on Realistic Mathematics Education to Improve Problem Solving Ability and Student Learning Independence. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education,14(1), 243-252.https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/4000
Hermawan, B. & Prihatmaji, Y. P. (2019). Perkembangan Bentukan Atap Rumah Tradisional Jawa.
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Desain dan Arsitektur (SENADA).
Julianto, E. N. (2015). Spirit Pluralisme dalam Klenteng Sam Poo Kong Semarang. The Messenger, 7(2), 36-41.http://dx.doi.org/10.26623/themessenger.v7i2.302
Khaliesh, H. (2014). Arsitektur Tradisional Tionghoa: Tinjauan Terhadap Identitas, Karakter Budaya dan Eksistensinya. Langkau Betang, 1(1), 86-99.
Kusmaryono, I. (2014). The Importance of Mathematical Power in Mathematics Learning. Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics, Science, and Education 2014 (ICMSE 2014). UNNES: 35–40.https://icmseunnes.com/2015/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/7.pdf
Marcella, B. S. (2014). Bentuk dan Makna Atap Kelenteng Sam Poo Kong Semarang. Jurnal Arsitektur KOMPOSISI, 10(5), 350-359. https://doi.org/10.24002/jars.v10i5.1094
Morris, T. & Paulsen, R.(2011). Using Tracing Paper to Teach Transformation Geometry. Amesa Vol. 2. Johannesburg: Amesa.
Naidoo, J. (2010). Strategies Used by Grade 12 Mathematics Learners in Transformation Geometry. Natal: University of Kwazulu.
Nejad, J. M., Zarghami, E., & Abad, A. S. H. (2016). A Study on the Concepts and Themes of Color and Light in the Exquisite Islamic Architecture. Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences, 8(3), 1077-1096. http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/jfas.v8i3.23
Nuraida, E. M. & Putri, R. I. (2020). The Context of Archipelago Traditional Cake to Explore Students' Understanding in Integers Division Class VII. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(1).https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.1.7400.91-10
Nursyahidah, F., Ilma, R., & Somakim. (2013). Supporting First Grade Student's Understanding of Addition up to 20 Using Traditional Game. Journal on Mathematics Education,4(2), 212–223. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.4.2.557.212-223
Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B. A., Albab, I. U., & Aisyah, F. (2020). Pengembangan Learning Trajectory Based Instruction Materi Kerucut Menggunakan Konteks Megono Gunungan. Mosharafa, JurnalPendidikanMatematika,9(1), 47-58.https://doi.org/10.31980/mosharafa.v9i1.560
Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B. A., & Rubowo, M. R. (2018). A Secondary Student's Problem Solving Ability in Learning Based on Realistic Mathematics with Ethnomathematics. Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education, 3(1), 13-24. https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v3i1.5607
Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B.A., & Albab, I.U., (2021a). Desain Pembelajaran Kerucut Berkonteks Tradisi Megono Gunungan. Jurnal Elemen,7(1), 14-27. https://doi.org/10.29408/jel.v7i1.2655
Nursyahidah, F., Saputro, B.A., & Albab, I.U., (2021b). Learning cylinder through the context of Giant Lopis tradition. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,1918. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1918/4/042086
Prahmana, R. C. I. (2010). Permainan “Tepuk Bergilir” yang berorientasikonstruktivisme dalam pembelajaran. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 4(2),1-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.22342/jpm.4.2.406.
Puspasari, L., Zulkardi, & Somakim. 2015. Desain Pembelajaran Luas Segi Banyak Menggunakan Tangram Berpetak di Kelas IV. Jurnal Inovasi Pembelajaran,1(2).https://doi.org/10.22219/jinop.v1i2.2566
Ramlan, A. M., & Hali, F. 2018. Analysis of the Difficulty of Mathematical Education Students in Completing the Geometric Running Problem Based on Van Hiele Theory in Geometry Transformation. Journal of Mathematics Education,3(2), 65-70. https://doi.org/10.31327/jomedu.v3i2.834
Risdiyanti, I., & Prahmana, R.C.I. (2020). The learning trajectory of number pattern learning using Barathayudha war stories and Uno Stacko. Journal on Mathematics Education,11(1), 157- 166.https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.11.1.10225.157-166
Wahidin dan Sugiman. (2014). Pengaruh Pendekatan PMRI terhadap Motivasi Berprestasi, Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah, dan Prestasi Belajar. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika,9(1).https://doi.org/10.21831/pg.v9i1.9072
Yanik, H. B. 2014. Middle-school students' concept images of geometric translations.TheJournal of Mathematical Behavior, 36, 33–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2014.08.001
Yeh et al. 2019.Enhancing achievement and interest in mathematics learning through Math- Island. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 14(1).https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-019-0100-9
Yeni, E.M. (2011). Pemanfaatan Benda-Benda Mnipulatif untuk Meningkatkan Pemahaman Konsep Geometri dan Kemampuan Tilikan Ruang Siswa kelas V Sekolah Dasar. Proceedings Simantap 2011. Medan: Indonesian Mathematical Society.
Zhang, D. (2019). Cultural Symbols in Chinese Architecture. Architecture and Design Review, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.18282/adr.v1i1.556
Zulkardi & Putri, R. I. (2006). Mendesain Sendiri Soal Kontekstual Matematika. Prosiding dalam Konferensi NasionalMatematika ke 13. Semarang: Universitas Negeri Semarang.