Main Article Content
Abstract
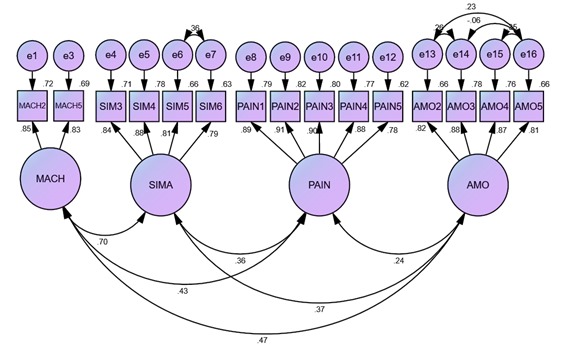
The study examines the influence of parental involvement and academic motivation on students' mathematics performance, mediated by students' interest in mathematics. The current study adopts a descriptive-correlational research design. The study population comprises all first-year and second-year senior high students in the Central Region of Ghana. A sample of 290 students was randomly selected from four senior high schools in the Central Region of Ghana. The researcher used stratified sampling techniques to categorize the students into the various courses offered in the schools and employed simple random sampling techniques to select respondents from each stratum for the study. A structured questionnaire was used as a research instrument to collect data from the target population. Analysis of Moment Structures (Amos) version 23 and IBM SPSS version 23 were used as analysis tools for data analysis. The analysis results show that parental involvement, academic motivation, and students' interest in mathematics have a significant positive effect on mathematics achievement. Furthermore, students' interest in mathematics partially mediates the link between parental involvement and mathematics achievement. Finally, students' interest in mathematics partially mediates the connection between mathematics motivation and mathematics achievement. The study recommends that parents must be fully involved in their children's education, especially in their mathematics learning, by providing students with the necessary support to improve their mathematics learning and performance.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Aguk, J., Onwonga, R., Chemining’wa, G., Jumbo, M., & Abong, G. (2021). Enhancing yellow maize production for sustainable food and nutrition security in Kenya. East African Journal of Science, Technology and Innovation, 2(May), 1–24.
- Alam, A., & Mohanty, A. (2023). Cultural beliefs and equity in educational institutions: exploring the social and philosophical notions of ability groupings in teaching and learning of mathematics. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 28(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/02673843.2023.2270662
- Amponsah, M. O., Milledzi, E. Y., Ampofo, E. T., & Gyambrah, M. (2018). Relationship between Parental Involvement and Academic Performance of Senior High School Students : The Case of Ashanti Mampong Municipality of Ghana. January. https://doi.org/10.12691/education-6-1-1
- Arthur, Y., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Assuah, C. (2017). Teacher-Student Variables as Predictor of Students’ Interest in Mathematics: The Use of Stepwise Multiple Linear Regression Analysis. Asian Research Journal of Mathematics, 4(3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.9734/arjom/2017/33544
- Arthur, Y. D. (2022). Modeling student ’ s interest in mathematics : Role of history of mathematics , peer- assisted learning , and student ’ s perception. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(10).
- Arthur, Y. D., Owusu, E. K., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Arhin, A. K. (2018). Connecting Mathematics To Real-Life Problems: A Teaching Quality That Improves Students’ Mathematics Interest. IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education, 8(4), 65–71. https://doi.org/10.9790/7388-0804026571
- Asare, B., Arthur, Y. D., & Boateng, F. O. (2023). Exploring the impact of chatgpt on mathematics performance: The influential role of student interest. Education Science and Management, 1(3), 158-168.
- Asvio, N. (2017). The Influence of Learning Motivation and Learning Environment on Undergraduate Students’ Learning Achievement of Management of Islamic Education, Study Program of Iain Batusangkar In 2016. Noble International Journal of Social Sciences Research ISSN, 2(2), 16–31.
- Bah, Y. M. (2022). Poor performance in mathematics among senior secondary school students: Lessons for education planners and parents. International Journal of Education and Learning, 4(1), 10–19. https://doi.org/10.31763/ijele.v4i1.605
- Bright, A., Welcome, N., & Arthur, Y. (2024). The effect of using technology in teaching and learning mathematics on student’s mathematics performance: The mediation effect of students’ mathematics interest. Journal of Mathematics and Science Teacher, 4(2).
- Callaman, R. A., & Itaas, E. C. (2020). Students’ mathematics achievement in Mindanao context: A meta-analysis. JRAMathEdu (Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education), 5(2), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v5i2.10282
- Casinillo, L. F., Palen, M. A. E., Casinillo, E. L., & Batidor, P. G. (2020). Assessing Senior High Student’s Learning Experiences in Mathematics. Indonesian Journal of Educational Studies, 23(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.26858/ijes.v23i1.13437
- Chand, S., Chaudhary, K., Prasad, A., & Chand, V. (2021). Perceived Causes of Students’ Poor Performance in Mathematics: A Case Study at Ba and Tavua Secondary Schools. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 7(April), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fams.2021.614408
- Chuang, S. (2021). The Applications of Constructivist Learning Theory and Social Learning Theory on Adult Continuous Development. Performance Improvement, 60(3), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/pfi.21963
- Cui, Y., Zhang, D., & Leung, F. K. S. (2021). The Influence of Parental Educational Involvement in Early Childhood on 4th Grade Students’ Mathematics Achievement. Early Education and Development, 32(1), 113–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2019.1677131
- Dewaele, J. M., & Li, C. (2021). Teacher enthusiasm and students’ social-behavioral learning engagement: The mediating role of student enjoyment and boredom in Chinese EFL classes. Language Teaching Research, 25(6), 922–945. https://doi.org/10.1177/13621688211014538
- Dietrichson, J., Filges, T., Seerup, J. K., Klokker, R. H., Viinholt, B. C. A., Bøg, M., & Eiberg, M. (2021). Targeted school-based interventions for improving reading and mathematics for students with or at risk of academic difficulties in Grades K-6: A systematic review. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 17(2). https://doi.org/10.1002/cl2.1152
- Du, C., Qin, K., Wang, Y., & Xin, T. (2021). Mathematics interest, anxiety, self-efficacy and achievement: Examining reciprocal relations. Learning and Individual Differences, 91(19), 102060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2021.102060
- El-adl, A., & Alkharusi, H. (2020). Relationships between Self-Regulated Learning Strategies, Learning Motivation and Mathematics Achievement, Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 2020. Eric - Ej1246489, 15(1), 104–111. https://eric.ed.gov/?q=learning+strategies&id=EJ1246489
- Fauth, B., Decristan, J., Decker, A. T., Büttner, G., Hardy, I., Klieme, E., & Kunter, M. (2019). The effects of teacher competence on student outcomes in elementary science education: The mediating role of teaching quality. Teaching and Teacher Education, 86, 102882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2019.102882
- Filgona, J., Sakiyo, J., Gwany, D. M., & Okoronka, A. U. (2020). Motivation in Learning. Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies, 10(4), 16–37. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajess/2020/v10i430273
- Fong, C. J., & Kremer, K. P. (2020). An Expectancy-Value Approach to Math Underachievement: Examining High School Achievement, College Attendance, and STEM Interest. Gifted Child Quarterly, 64(2), 67–84. https://doi.org/10.1177/0016986219890599
- Fosu, M., Arthur, Y. D., Boateng, F. O., & Adu-Obeng, B. (2022). Mediation and moderation effect of mathematics interest and teaching quality between self-concept and mathematics achievement. Journal of Mathematics and Science Teacher, 3(1), em024. https://doi.org/10.29333/mathsciteacher/12622
- Ghasemi, F. (2021). A motivational response to the inefficiency of teachers’ practices towards students with learned helplessness. Learning and Motivation, 73(May 2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lmot.2020.101705
- Gonzalez-DeHass, A., Willems, P., & Holbein, M. (2005). Examining the Relationship Between Parental Involvement and Student Motivation. Educational Psychology Review, 17, 99-123. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10648-005-3949-7.
- Guo, J., Marsh, H., Parker, P., Morin, A., & Yeung, A. (2015). Expectancy-value in mathematics, gender and socioeconomic background as predictors of achievement and aspirations : A multi-cohort study. Learning and Individual Differences, 37, 161-168. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LINDIF.2015.01.008.
- Guskey, T. R. (1988). Teacher efficacy, self-concept, and attitudes toward the implementation of instructional innovation. Teaching and Teacher Education, 4(1), 63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0742-051X(88)90025-X
- Habók, A., Magyar, A., Németh, M. B., & Csapó, B. (2020). Motivation and self-related beliefs as predictors of academic achievement in reading and mathematics: Structural equation models of longitudinal data. International Journal of Educational Research, 103(February), 101634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101634
- Heyder, A., Weidinger, A. F., & Steinmayr, R. (2021). Only a Burden for Females in Math? Gender and Domain Differences in the Relation Between Adolescents’ Fixed Mindsets and Motivation. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 50(1), 177–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01345-4
- Higgins, K., Huscroft-D’Angelo, J., & Crawford, L. (2019). Effects of Technology in Mathematics on Achievement, Motivation, and Attitude: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57(2), 283–319. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633117748416
- Igwe, A., & Joseph, V. (2019). Students’ perception of teachers effectiveness and learning outcomes in mathematics and economics in secondary schools of cross river state, nigeria. 2(1).
- Jiang, S., Simpkins, S. D., & Eccles, J. S. (2020). Individuals’ math and science motivation and their subsequent STEM choices and achievement in high school and college: A longitudinal study of gender and college generation status differences. Developmental Psychology, 56(11), 2137–2151. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0001110
- Kelley, T. R., Knowles, J. G., Holland, J. D., & Han, J. (2020). Increasing high school teachers self-efficacy for integrated STEM instruction through a collaborative community of practice. International Journal of STEM Education, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00211-w
- Kim, J. I., & Chung, H. (2012). The role of family orientation in predicting Korean boys’ and girls’ achievement motivation to learn mathematics. Learning and Individual Differences, 22(1), 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.11.009
- Kim, S. W. (2020). Meta-Analysis of Parental Involvement and Achievement in East Asian Countries. Education and Urban Society, 52(2), 312–337. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013124519842654
- Kline, R. B. (2018). Response to Leslie Hayduk’s review of principles and practice of structural equation modeling,1 4th edition. Canadian Studies in Population, 45(3–4), 188–195. https://doi.org/10.25336/csp29418
- Kosel, C., Wolter, I., & Seidel, T. (2021). Profiling secondary school students in mathematics and German language arts using learning-relevant cognitive and motivational-affective characteristics. Learning and Instruction, 73(October 2020), 101434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2020.101434
- Lara, L., & Saracostti, M. (2019). Effect of parental involvement on children’s academic achievement in Chile. Frontiers in Psychology, 10(JUN), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01464
- Lo, C. K., & Hew, K. F. (2021). Developing a flipped learning approach to support student engagement: A design-based research of secondary school mathematics teaching. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 37(1), 142–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12474
- Matriano, E. A. (2020). Ensuring Student-Centered, Constructivist and Project-Based Experiential Learning Applying the Exploration, Research, Interaction and Creation (ERIC) Learning Model. International Online Journal of Education and Teaching, 7(1), 214–227. http://iojet.org/index.php/IOJET/article/view/727
- Mokhtar, S. F., Yusof, Z. M., & Misiran, M. (2012). Factors affecting students’ performance in mathematics. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 8(8), 4133–4137.
- Ocampo, E. N., Mobo, F. D., & Cutillas, A. L. (2023). Exploring the Relationship Between Mathematics Performance and Learn-ing Style Among Grade 8 Students. International Journal of Multidisciplinary: Applied Business and Education Research, 4(4), 1165–1172. https://doi.org/10.11594/ijmaber.04.04.14
- Ozkal, N. (2019). Relationships between self-efficacy beliefs, engagement and academic performance in math lessons. Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 14(2), 190–200. https://doi.org/10.18844/cjes.v14i2.3766
- Panaoura, R. (2021). Parental Involvement in Children ’ s Mathematics Learning Before and During the Period of the COVID-19. 2(1), 65–74.
- Perera, H. N., & John, J. E. (2020). Teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs for teaching math: Relations with teacher and student outcomes. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 61, 101842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2020.101842
- Ramzan, M., Javaid, Z. K., Kareem, A., & Mobeen, S. (2023). Amplifying Classroom Enjoyment and Cultivating Positive Learning Attitudes among ESL Learners. Pakistan Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 11(2), 2298–2308. https://doi.org/10.52131/pjhss.2023.1102.0522
- Ran, H., Kasli, M., & Secada, W. G. (2021). A Meta-Analysis on Computer Technology Intervention Effects on Mathematics Achievement for Low-Performing Students in K-12 Classrooms. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 59(1), 119–153. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633120952063
- Saleem, F. T., Howard, T. C., & Langley, A. K. (2022). Understanding and addressing racial stress and trauma in schools: A pathway toward resistance and healing. Psychology in the Schools, 59(12), 2506–2521. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22615
- Silinskas, G., & Kikas, E. (2019). Parental Involvement in Math Homework: Links to Children’s Performance and Motivation. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 63(1), 17–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/00313831.2017.1324901
- Šimunović, M., & Babarović, T. (2020). The role of parents’ beliefs in students’ motivation, achievement, and choices in the STEM domain: a review and directions for future research. Social Psychology of Education, 23(3), 701–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-020-09555-1
- Suren, N., & Kandemir, A.M. (2020). The effects of mathematics anxiety and motivation on students’ mathematics achievement. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology, 8(3), 190–218. https://doi.org/10.46328/IJEMST.V8I3.926
- Tan, C. Y., Lyu, M., & Peng, B. (2020). Academic Benefits from Parental Involvement are Stratified by Parental Socioeconomic Status : A Meta-analysis Academic Benefits from Parental Involvement are Stratified by Parental Socioeconomic Status : A Meta-analysis. Parenting, 20(4), 241–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2019.1694836
- Tang, M., Wang, D., & Guerrien, A. (2020). A systematic review and meta-analysis on basic psychological need satisfaction, motivation, and well-being in later life: Contributions of self-determination theory. PsyCh Journal, 9(1), 5–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.293
- Tella, A. (2007). The Impact of Motivation on Student's Academic Achievement and Learning Outcomes in Mathematics among Secondary School Students in Nigeria. Eurasia journal of mathematics, science and technology education, 3, 149-156. https://doi.org/10.12973/EJMSTE/75390.
- Teodorović, J., Milin, V., Bodroža, B., Đerić, I. D., Vujačić, M., Jakšić, I. M., Stanković, D., Cankar, G., Charalambous, C. Y., Damme, J. Van, & Kyriakides, L. (2022). Testing the dynamic model of educational effectiveness: the impact of teacher factors on interest and achievement in mathematics and biology in Serbia. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 33(1), 51–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2021.1942076
- Tucker-Drob, E. M., & Harden, K. P. (2012). Learning motivation mediates gene-by-socioeconomic status interaction on mathematics achievement in early childhood. Learning and Individual Differences, 22(1), 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.11.015
- Vaiopoulou, J., Papadakis, S., Sifaki, E., Stamovlasis, D., & Kalogiannakis, M. (2021). Parents’ perceptions of educational apps use for kindergarten children: Development and validation of a new instrument (peau-p) and exploration of parents’ profiles. Behavioral Sciences, 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11060082
- Villa, F. T., & Tulod, R. C. (2021). Correlating instructional leadership practices of school administrators with teachers competencies. Linguistics and Culture Review, 5(S1), 83–99. https://doi.org/10.21744/lingcure.v5ns1.1318
- Walter, J., & Hart, J. (2009). Understanding the complexities of student motivations in mathematics learning. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 28, 162-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMATHB.2009.07.001.
- Wang, G., Zhang, S., & Cai, J. (2021). How are parental expectations related to students’ beliefs and their perceived achievement? Educational Studies in Mathematics, 108(3), 429–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-021-10073-w
- Williams, K., & Williams, H. (2021). Mathematics problem-solving homework as a conduit for parental involvement in learning. Evaluation of a pilot study. Educational Review, 73(2), 209–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2019.1566210
- Wong, S. L., & Wong, S. L. (2019). Relationship between interest and mathematics performance in a technology-enhanced learning context in Malaysia. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-019-0114-3
- Wright, K. B., Shields, S. M., Black, K., & Waxman, H. C. (2018). The Effects of Teacher Home Visits on Student Behavior , Student Academic Achievement , and Parent Involvement. 28(1), 67–90.
- Wu, F., Jiang, Y., Liu, D., Konorova, E., & Yang, X. (2022). The role of perceived teacher and peer relationships in adolescent students’ academic motivation and educational outcomes. Educational Psychology, 42(4), 439–458. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2022.2042488
- Yu, M. V. B., Liu, Y., Soto-Lara, S., Puente, K., Carranza, P., Pantano, A., & Simpkins, S. D. (2021). Culturally Responsive Practices: Insights from a High-Quality Math Afterschool Program Serving Underprivileged Latinx Youth. American Journal of Community Psychology, 68(3–4), 323–339. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajcp.12518
- Zhang, D., & Wang, C. (2020). The relationship between mathematics interest and mathematics achievement: mediating roles of self-efficacy and mathematics anxiety. International Journal of Educational Research, 104(July), 101648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101648
References
Aguk, J., Onwonga, R., Chemining’wa, G., Jumbo, M., & Abong, G. (2021). Enhancing yellow maize production for sustainable food and nutrition security in Kenya. East African Journal of Science, Technology and Innovation, 2(May), 1–24.
Alam, A., & Mohanty, A. (2023). Cultural beliefs and equity in educational institutions: exploring the social and philosophical notions of ability groupings in teaching and learning of mathematics. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 28(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/02673843.2023.2270662
Amponsah, M. O., Milledzi, E. Y., Ampofo, E. T., & Gyambrah, M. (2018). Relationship between Parental Involvement and Academic Performance of Senior High School Students : The Case of Ashanti Mampong Municipality of Ghana. January. https://doi.org/10.12691/education-6-1-1
Arthur, Y., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Assuah, C. (2017). Teacher-Student Variables as Predictor of Students’ Interest in Mathematics: The Use of Stepwise Multiple Linear Regression Analysis. Asian Research Journal of Mathematics, 4(3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.9734/arjom/2017/33544
Arthur, Y. D. (2022). Modeling student ’ s interest in mathematics : Role of history of mathematics , peer- assisted learning , and student ’ s perception. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(10).
Arthur, Y. D., Owusu, E. K., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Arhin, A. K. (2018). Connecting Mathematics To Real-Life Problems: A Teaching Quality That Improves Students’ Mathematics Interest. IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education, 8(4), 65–71. https://doi.org/10.9790/7388-0804026571
Asare, B., Arthur, Y. D., & Boateng, F. O. (2023). Exploring the impact of chatgpt on mathematics performance: The influential role of student interest. Education Science and Management, 1(3), 158-168.
Asvio, N. (2017). The Influence of Learning Motivation and Learning Environment on Undergraduate Students’ Learning Achievement of Management of Islamic Education, Study Program of Iain Batusangkar In 2016. Noble International Journal of Social Sciences Research ISSN, 2(2), 16–31.
Bah, Y. M. (2022). Poor performance in mathematics among senior secondary school students: Lessons for education planners and parents. International Journal of Education and Learning, 4(1), 10–19. https://doi.org/10.31763/ijele.v4i1.605
Bright, A., Welcome, N., & Arthur, Y. (2024). The effect of using technology in teaching and learning mathematics on student’s mathematics performance: The mediation effect of students’ mathematics interest. Journal of Mathematics and Science Teacher, 4(2).
Callaman, R. A., & Itaas, E. C. (2020). Students’ mathematics achievement in Mindanao context: A meta-analysis. JRAMathEdu (Journal of Research and Advances in Mathematics Education), 5(2), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.23917/jramathedu.v5i2.10282
Casinillo, L. F., Palen, M. A. E., Casinillo, E. L., & Batidor, P. G. (2020). Assessing Senior High Student’s Learning Experiences in Mathematics. Indonesian Journal of Educational Studies, 23(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.26858/ijes.v23i1.13437
Chand, S., Chaudhary, K., Prasad, A., & Chand, V. (2021). Perceived Causes of Students’ Poor Performance in Mathematics: A Case Study at Ba and Tavua Secondary Schools. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 7(April), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fams.2021.614408
Chuang, S. (2021). The Applications of Constructivist Learning Theory and Social Learning Theory on Adult Continuous Development. Performance Improvement, 60(3), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/pfi.21963
Cui, Y., Zhang, D., & Leung, F. K. S. (2021). The Influence of Parental Educational Involvement in Early Childhood on 4th Grade Students’ Mathematics Achievement. Early Education and Development, 32(1), 113–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2019.1677131
Dewaele, J. M., & Li, C. (2021). Teacher enthusiasm and students’ social-behavioral learning engagement: The mediating role of student enjoyment and boredom in Chinese EFL classes. Language Teaching Research, 25(6), 922–945. https://doi.org/10.1177/13621688211014538
Dietrichson, J., Filges, T., Seerup, J. K., Klokker, R. H., Viinholt, B. C. A., Bøg, M., & Eiberg, M. (2021). Targeted school-based interventions for improving reading and mathematics for students with or at risk of academic difficulties in Grades K-6: A systematic review. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 17(2). https://doi.org/10.1002/cl2.1152
Du, C., Qin, K., Wang, Y., & Xin, T. (2021). Mathematics interest, anxiety, self-efficacy and achievement: Examining reciprocal relations. Learning and Individual Differences, 91(19), 102060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2021.102060
El-adl, A., & Alkharusi, H. (2020). Relationships between Self-Regulated Learning Strategies, Learning Motivation and Mathematics Achievement, Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 2020. Eric - Ej1246489, 15(1), 104–111. https://eric.ed.gov/?q=learning+strategies&id=EJ1246489
Fauth, B., Decristan, J., Decker, A. T., Büttner, G., Hardy, I., Klieme, E., & Kunter, M. (2019). The effects of teacher competence on student outcomes in elementary science education: The mediating role of teaching quality. Teaching and Teacher Education, 86, 102882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2019.102882
Filgona, J., Sakiyo, J., Gwany, D. M., & Okoronka, A. U. (2020). Motivation in Learning. Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies, 10(4), 16–37. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajess/2020/v10i430273
Fong, C. J., & Kremer, K. P. (2020). An Expectancy-Value Approach to Math Underachievement: Examining High School Achievement, College Attendance, and STEM Interest. Gifted Child Quarterly, 64(2), 67–84. https://doi.org/10.1177/0016986219890599
Fosu, M., Arthur, Y. D., Boateng, F. O., & Adu-Obeng, B. (2022). Mediation and moderation effect of mathematics interest and teaching quality between self-concept and mathematics achievement. Journal of Mathematics and Science Teacher, 3(1), em024. https://doi.org/10.29333/mathsciteacher/12622
Ghasemi, F. (2021). A motivational response to the inefficiency of teachers’ practices towards students with learned helplessness. Learning and Motivation, 73(May 2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lmot.2020.101705
Gonzalez-DeHass, A., Willems, P., & Holbein, M. (2005). Examining the Relationship Between Parental Involvement and Student Motivation. Educational Psychology Review, 17, 99-123. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10648-005-3949-7.
Guo, J., Marsh, H., Parker, P., Morin, A., & Yeung, A. (2015). Expectancy-value in mathematics, gender and socioeconomic background as predictors of achievement and aspirations : A multi-cohort study. Learning and Individual Differences, 37, 161-168. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LINDIF.2015.01.008.
Guskey, T. R. (1988). Teacher efficacy, self-concept, and attitudes toward the implementation of instructional innovation. Teaching and Teacher Education, 4(1), 63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0742-051X(88)90025-X
Habók, A., Magyar, A., Németh, M. B., & Csapó, B. (2020). Motivation and self-related beliefs as predictors of academic achievement in reading and mathematics: Structural equation models of longitudinal data. International Journal of Educational Research, 103(February), 101634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101634
Heyder, A., Weidinger, A. F., & Steinmayr, R. (2021). Only a Burden for Females in Math? Gender and Domain Differences in the Relation Between Adolescents’ Fixed Mindsets and Motivation. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 50(1), 177–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01345-4
Higgins, K., Huscroft-D’Angelo, J., & Crawford, L. (2019). Effects of Technology in Mathematics on Achievement, Motivation, and Attitude: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57(2), 283–319. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633117748416
Igwe, A., & Joseph, V. (2019). Students’ perception of teachers effectiveness and learning outcomes in mathematics and economics in secondary schools of cross river state, nigeria. 2(1).
Jiang, S., Simpkins, S. D., & Eccles, J. S. (2020). Individuals’ math and science motivation and their subsequent STEM choices and achievement in high school and college: A longitudinal study of gender and college generation status differences. Developmental Psychology, 56(11), 2137–2151. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0001110
Kelley, T. R., Knowles, J. G., Holland, J. D., & Han, J. (2020). Increasing high school teachers self-efficacy for integrated STEM instruction through a collaborative community of practice. International Journal of STEM Education, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00211-w
Kim, J. I., & Chung, H. (2012). The role of family orientation in predicting Korean boys’ and girls’ achievement motivation to learn mathematics. Learning and Individual Differences, 22(1), 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.11.009
Kim, S. W. (2020). Meta-Analysis of Parental Involvement and Achievement in East Asian Countries. Education and Urban Society, 52(2), 312–337. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013124519842654
Kline, R. B. (2018). Response to Leslie Hayduk’s review of principles and practice of structural equation modeling,1 4th edition. Canadian Studies in Population, 45(3–4), 188–195. https://doi.org/10.25336/csp29418
Kosel, C., Wolter, I., & Seidel, T. (2021). Profiling secondary school students in mathematics and German language arts using learning-relevant cognitive and motivational-affective characteristics. Learning and Instruction, 73(October 2020), 101434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2020.101434
Lara, L., & Saracostti, M. (2019). Effect of parental involvement on children’s academic achievement in Chile. Frontiers in Psychology, 10(JUN), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01464
Lo, C. K., & Hew, K. F. (2021). Developing a flipped learning approach to support student engagement: A design-based research of secondary school mathematics teaching. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 37(1), 142–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12474
Matriano, E. A. (2020). Ensuring Student-Centered, Constructivist and Project-Based Experiential Learning Applying the Exploration, Research, Interaction and Creation (ERIC) Learning Model. International Online Journal of Education and Teaching, 7(1), 214–227. http://iojet.org/index.php/IOJET/article/view/727
Mokhtar, S. F., Yusof, Z. M., & Misiran, M. (2012). Factors affecting students’ performance in mathematics. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 8(8), 4133–4137.
Ocampo, E. N., Mobo, F. D., & Cutillas, A. L. (2023). Exploring the Relationship Between Mathematics Performance and Learn-ing Style Among Grade 8 Students. International Journal of Multidisciplinary: Applied Business and Education Research, 4(4), 1165–1172. https://doi.org/10.11594/ijmaber.04.04.14
Ozkal, N. (2019). Relationships between self-efficacy beliefs, engagement and academic performance in math lessons. Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 14(2), 190–200. https://doi.org/10.18844/cjes.v14i2.3766
Panaoura, R. (2021). Parental Involvement in Children ’ s Mathematics Learning Before and During the Period of the COVID-19. 2(1), 65–74.
Perera, H. N., & John, J. E. (2020). Teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs for teaching math: Relations with teacher and student outcomes. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 61, 101842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2020.101842
Ramzan, M., Javaid, Z. K., Kareem, A., & Mobeen, S. (2023). Amplifying Classroom Enjoyment and Cultivating Positive Learning Attitudes among ESL Learners. Pakistan Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 11(2), 2298–2308. https://doi.org/10.52131/pjhss.2023.1102.0522
Ran, H., Kasli, M., & Secada, W. G. (2021). A Meta-Analysis on Computer Technology Intervention Effects on Mathematics Achievement for Low-Performing Students in K-12 Classrooms. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 59(1), 119–153. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633120952063
Saleem, F. T., Howard, T. C., & Langley, A. K. (2022). Understanding and addressing racial stress and trauma in schools: A pathway toward resistance and healing. Psychology in the Schools, 59(12), 2506–2521. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22615
Silinskas, G., & Kikas, E. (2019). Parental Involvement in Math Homework: Links to Children’s Performance and Motivation. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 63(1), 17–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/00313831.2017.1324901
Šimunović, M., & Babarović, T. (2020). The role of parents’ beliefs in students’ motivation, achievement, and choices in the STEM domain: a review and directions for future research. Social Psychology of Education, 23(3), 701–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-020-09555-1
Suren, N., & Kandemir, A.M. (2020). The effects of mathematics anxiety and motivation on students’ mathematics achievement. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology, 8(3), 190–218. https://doi.org/10.46328/IJEMST.V8I3.926
Tan, C. Y., Lyu, M., & Peng, B. (2020). Academic Benefits from Parental Involvement are Stratified by Parental Socioeconomic Status : A Meta-analysis Academic Benefits from Parental Involvement are Stratified by Parental Socioeconomic Status : A Meta-analysis. Parenting, 20(4), 241–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2019.1694836
Tang, M., Wang, D., & Guerrien, A. (2020). A systematic review and meta-analysis on basic psychological need satisfaction, motivation, and well-being in later life: Contributions of self-determination theory. PsyCh Journal, 9(1), 5–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.293
Tella, A. (2007). The Impact of Motivation on Student's Academic Achievement and Learning Outcomes in Mathematics among Secondary School Students in Nigeria. Eurasia journal of mathematics, science and technology education, 3, 149-156. https://doi.org/10.12973/EJMSTE/75390.
Teodorović, J., Milin, V., Bodroža, B., Đerić, I. D., Vujačić, M., Jakšić, I. M., Stanković, D., Cankar, G., Charalambous, C. Y., Damme, J. Van, & Kyriakides, L. (2022). Testing the dynamic model of educational effectiveness: the impact of teacher factors on interest and achievement in mathematics and biology in Serbia. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 33(1), 51–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2021.1942076
Tucker-Drob, E. M., & Harden, K. P. (2012). Learning motivation mediates gene-by-socioeconomic status interaction on mathematics achievement in early childhood. Learning and Individual Differences, 22(1), 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.11.015
Vaiopoulou, J., Papadakis, S., Sifaki, E., Stamovlasis, D., & Kalogiannakis, M. (2021). Parents’ perceptions of educational apps use for kindergarten children: Development and validation of a new instrument (peau-p) and exploration of parents’ profiles. Behavioral Sciences, 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11060082
Villa, F. T., & Tulod, R. C. (2021). Correlating instructional leadership practices of school administrators with teachers competencies. Linguistics and Culture Review, 5(S1), 83–99. https://doi.org/10.21744/lingcure.v5ns1.1318
Walter, J., & Hart, J. (2009). Understanding the complexities of student motivations in mathematics learning. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 28, 162-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMATHB.2009.07.001.
Wang, G., Zhang, S., & Cai, J. (2021). How are parental expectations related to students’ beliefs and their perceived achievement? Educational Studies in Mathematics, 108(3), 429–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-021-10073-w
Williams, K., & Williams, H. (2021). Mathematics problem-solving homework as a conduit for parental involvement in learning. Evaluation of a pilot study. Educational Review, 73(2), 209–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2019.1566210
Wong, S. L., & Wong, S. L. (2019). Relationship between interest and mathematics performance in a technology-enhanced learning context in Malaysia. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-019-0114-3
Wright, K. B., Shields, S. M., Black, K., & Waxman, H. C. (2018). The Effects of Teacher Home Visits on Student Behavior , Student Academic Achievement , and Parent Involvement. 28(1), 67–90.
Wu, F., Jiang, Y., Liu, D., Konorova, E., & Yang, X. (2022). The role of perceived teacher and peer relationships in adolescent students’ academic motivation and educational outcomes. Educational Psychology, 42(4), 439–458. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2022.2042488
Yu, M. V. B., Liu, Y., Soto-Lara, S., Puente, K., Carranza, P., Pantano, A., & Simpkins, S. D. (2021). Culturally Responsive Practices: Insights from a High-Quality Math Afterschool Program Serving Underprivileged Latinx Youth. American Journal of Community Psychology, 68(3–4), 323–339. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajcp.12518
Zhang, D., & Wang, C. (2020). The relationship between mathematics interest and mathematics achievement: mediating roles of self-efficacy and mathematics anxiety. International Journal of Educational Research, 104(July), 101648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101648