Main Article Content
Abstract
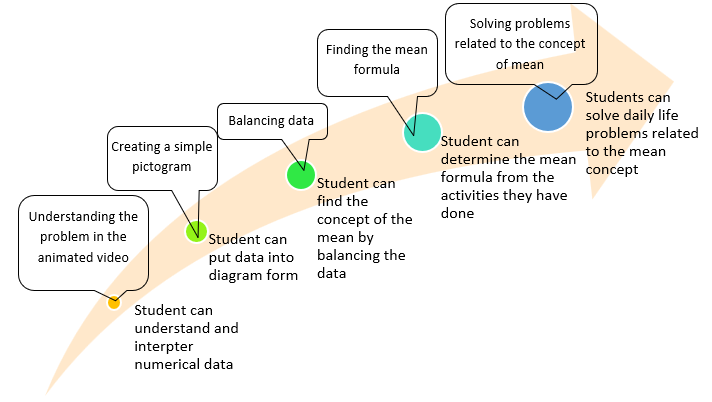
Conceptual understanding is a critical component of effective mathematics learning. However, many students encounter challenges in understanding mathematical concepts, including the concept of the mean. This study aims to design a learning trajectory that enhances students’ conceptual understanding of the mean. Employing a design research methodology, the study followed the stages of validation studies in creating and refining a hypothetical learning trajectory (HLT). The research consisted of three stages: preliminary design, design experiment (encompassing pilot experiment and teaching experiment), and retrospective analysis. The participants were fourty eighth-grade students from a public school in Cimahi. Data were collected through interviews, observations, documentation, and field notes, which informed iterative improvement to the HLT. Data analysis involved comparing students’ actual learning experiences with the HLT as a reference framework. The findings reveal that integrating technology and problem-based learning enhances students’ conceptual understanding of the mean, fostering creativity and real-world problem-solving skills. Based on these results, this study proposes a validated learning trajectory to support students in developing a deeper conceptual understanding of the mean.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2025 Usman Aripin, Tanti Rosmiati, Euis Eti Rohaeti, Wahyu Hidayat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Adelia, V., Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, Z., & Mulyono, B. (2022). Learning trajectory for equivalent fraction learning: An insight. Journal of Honai Math, 5(1), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.30862/jhm.v5i1.233
- Adha, I.,Zulkardi, Putri, R. I. I., & Somakim. (2024). A learning trajectory for surface area concept with the context of the tourist destination Bukit Sulap. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(3),409-430. https://doi.org/10.23107/jpm.v18i3.pp409-430
- Alshatri, S. H., Wakil, K., Jamal, K. & Bakhtyar, R. (2019). Teaching aids effectiveness in learning mathematics. International Journal of Educational Research Review, 4(3), 448-453. https://doi.org/10.24331/ijere.573949
- Aripin, U., Zulkardi, Z., Putri, R. I. I., & Hendriana, H. (2024). How is the learning evaluation of the Pythagorean theorem?: A systematic literature review. Jurnal Pendidikan MIPA, 25(2), 847-863. http://dx.doi.org/10.23960/jpmipa/v25i2.pp847-863
- Arnold, P., & Franklin, C. (2021). What makes a good statistical question?. Journal of Statistics and Data Science Education, 29(1), 122-130. https://doi.org/10.1080/26939169.2021.1877582
- Ashaver, D., & Igyuve, S. M. (2013). The use of audio-visual materials in the teaching and learning processes in colleges of education in Benue State-Nigeria. IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education (IOSRJRME), 1(6), 44–55. https://doi.org/10.9790/7388-0164455
- Backfisch, I., Lachner, A., Hische, C., Loose, F., & Scheiter, K. (2020). Professional knowledge or motivation? Investigating the role of teachers’ expertise on the quality of technology-enhanced lesson plans. Learning and Instruction, 66(December 2019), 101300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2019.101300
- Blum, W. & Leiβ, D. (2007). How do students and teachers deal with modelling problems? In Mathematical Modelling: Education, Engineering and Economics; Haines, C., Galbraith, P., Blum, W., Khan, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Chichester, UK,
- Cipta, E. S., Suryadi, D., Herman, T., Jupri, A., Konidah, E., Chusaery, H. A., Haryadi, H., & Sarinah, S. (2024). Enhancing students'understanding of the mean concept through problem-based learning assisted by Geogebra: A quasi-experimental study. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology (JESTEC), 19(5). https://jestec.taylors.edu.my/Special%20Issue%20ISCoE%202023_3/ISCoE%202023%203_03.pdf
- Cooper, L., & Shore, F. S. (2008). Students' misconceptions in interpreting center and variability of data represented via histograms and stem-and-leaf plots. Journal of Statistics Education, 16(2). https://doi.org/10.1080/10691898.2008.11889559
- Gravemeijer, K., & Eerde, D. van. (2009). Design research as a means for building a knowledge base for teachers and teaching in mathematics education. The Elementary School Journal, 109(5), 510–524. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1086/596999
- Kumar, L. A., Renuka, D. K., Rose, S. L., & Wartana, I. M. (2022). Deep learning based assistive technology on audio visual speech recognition for hearing impaired. International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, 3(1), 24-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcce.2022.01.003
- Lehrer, R., Kim, M. J., & Jones, R. S. (2011). Developing conceptions of statistics by designing measures of distribution. ZDM, 43, 723-736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-011-0347-0
- Li, X., Zhou, Y., & Chen, M. (2021). Validation and Implementation of Hawgent on Pythagoras Theorem. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2123(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2123/1/012042
- Livingston, E. H. (2004). The mean and standard deviation: what does it all mean?. Journal of Surgical Research, 119(2), 117-123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2004.02.008
- Martinez, M. N., & Bartholomew, M. J. (2017). What does it “mean”? A review of interpreting and calculating different types of means and standard deviations. Pharmaceutics, 9(2), 1-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9020014
- McGatha, M., Cobb, P., & McClain, K. (2002). An analysis of students’ initial statistical understandings: Developing a conjectured learning trajectory. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 21(3), 339-355. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0732-3123(02)00133-5
- Mustaffa, N., Ismail, Z., Tasir, Z., & Said, M. N. H. M. (2016). The impacts of implementing problem-based learning (PBL) in mathematics: A review of literature. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 6(12), 490-503. http://dx.doi.org/10.6007/IJARBSS/v6-i12/2513
- Napitupulu, E.E., Suryadi, D., & Kusumah, Y.S. (2016). Cultivating Upper Secondary Students’ Mathematical Reasoning -Ability and Attitude towards Mathematics through Problem-Based Learning. Journal on Mathematics Education, 7(2), 117-128 https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.7.2.3542.117-128
- Nurin, N. S., Junaedi, I., & Cahyono, A. N. (2024). Learning numeracy around school environment supported by mobile math trails using problem-based learning model. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(3), 485-498. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i3.pp485-498
- Oberlander, J., & Talbert-Johnson, C. (2004). Using technology to support problem-based learning. Action in teacher education, 25(4), 48-57. https://doi.org/10.1080/01626620.2004.10648296
- Plomp, T., & Nieveen, N. (2013). Educational design research: An introduction. Educational design research. Enschede, The Netherlands: SLO
- Putri, R. I. I., & Zulkardi. (2017). Fraction in shot-put: A learning trajectory. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1868, 050005. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995132
- Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, & Riskanita, A. D. (2022). Students’ problem-solving ability in solving algebra tasks using the context of Palembang. Journal on Mathematics Education, 13(3), 549–564. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v13i3.pp549-564
- Risdiyanti, I., & Prahmana, R. C. I. (2021). Designing learning trajectory of set through the indonesian shadow puppets and mahabharata stories. Infinity Journal, 10(2), 331-348. http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9093-5851
- Sari, A., & Putri, R. I. I. (2021). Inductive reasoning ability of students using the Palembang songket fabric context in rotational learning in grade IX. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(1), 57–72. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.14304.57-72
- Schoen, R. C., Rhoads, C., Perez, A., Jacobbe, T., & Li, L. (2025). Improving the teaching and learning of statistics. Learning and Instruction, 95, 102018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2024.102018
- Taleb, Z., Ahmadi, A., & Musavi, M. (2015). The effect of m-learning on mathematics learning. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 171, 83-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.092
- Ulfah, A. S., Yerizon, Y., & Arnawa, I. M. (2020). Preliminary research of mathematics learning device development based on Realistic Mathematics Education (RME). Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1554, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1554/1/012027
References
Adelia, V., Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, Z., & Mulyono, B. (2022). Learning trajectory for equivalent fraction learning: An insight. Journal of Honai Math, 5(1), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.30862/jhm.v5i1.233
Adha, I.,Zulkardi, Putri, R. I. I., & Somakim. (2024). A learning trajectory for surface area concept with the context of the tourist destination Bukit Sulap. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(3),409-430. https://doi.org/10.23107/jpm.v18i3.pp409-430
Alshatri, S. H., Wakil, K., Jamal, K. & Bakhtyar, R. (2019). Teaching aids effectiveness in learning mathematics. International Journal of Educational Research Review, 4(3), 448-453. https://doi.org/10.24331/ijere.573949
Aripin, U., Zulkardi, Z., Putri, R. I. I., & Hendriana, H. (2024). How is the learning evaluation of the Pythagorean theorem?: A systematic literature review. Jurnal Pendidikan MIPA, 25(2), 847-863. http://dx.doi.org/10.23960/jpmipa/v25i2.pp847-863
Arnold, P., & Franklin, C. (2021). What makes a good statistical question?. Journal of Statistics and Data Science Education, 29(1), 122-130. https://doi.org/10.1080/26939169.2021.1877582
Ashaver, D., & Igyuve, S. M. (2013). The use of audio-visual materials in the teaching and learning processes in colleges of education in Benue State-Nigeria. IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education (IOSRJRME), 1(6), 44–55. https://doi.org/10.9790/7388-0164455
Backfisch, I., Lachner, A., Hische, C., Loose, F., & Scheiter, K. (2020). Professional knowledge or motivation? Investigating the role of teachers’ expertise on the quality of technology-enhanced lesson plans. Learning and Instruction, 66(December 2019), 101300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2019.101300
Blum, W. & Leiβ, D. (2007). How do students and teachers deal with modelling problems? In Mathematical Modelling: Education, Engineering and Economics; Haines, C., Galbraith, P., Blum, W., Khan, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Chichester, UK,
Cipta, E. S., Suryadi, D., Herman, T., Jupri, A., Konidah, E., Chusaery, H. A., Haryadi, H., & Sarinah, S. (2024). Enhancing students'understanding of the mean concept through problem-based learning assisted by Geogebra: A quasi-experimental study. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology (JESTEC), 19(5). https://jestec.taylors.edu.my/Special%20Issue%20ISCoE%202023_3/ISCoE%202023%203_03.pdf
Cooper, L., & Shore, F. S. (2008). Students' misconceptions in interpreting center and variability of data represented via histograms and stem-and-leaf plots. Journal of Statistics Education, 16(2). https://doi.org/10.1080/10691898.2008.11889559
Gravemeijer, K., & Eerde, D. van. (2009). Design research as a means for building a knowledge base for teachers and teaching in mathematics education. The Elementary School Journal, 109(5), 510–524. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1086/596999
Kumar, L. A., Renuka, D. K., Rose, S. L., & Wartana, I. M. (2022). Deep learning based assistive technology on audio visual speech recognition for hearing impaired. International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, 3(1), 24-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcce.2022.01.003
Lehrer, R., Kim, M. J., & Jones, R. S. (2011). Developing conceptions of statistics by designing measures of distribution. ZDM, 43, 723-736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-011-0347-0
Li, X., Zhou, Y., & Chen, M. (2021). Validation and Implementation of Hawgent on Pythagoras Theorem. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2123(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2123/1/012042
Livingston, E. H. (2004). The mean and standard deviation: what does it all mean?. Journal of Surgical Research, 119(2), 117-123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2004.02.008
Martinez, M. N., & Bartholomew, M. J. (2017). What does it “mean”? A review of interpreting and calculating different types of means and standard deviations. Pharmaceutics, 9(2), 1-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9020014
McGatha, M., Cobb, P., & McClain, K. (2002). An analysis of students’ initial statistical understandings: Developing a conjectured learning trajectory. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 21(3), 339-355. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0732-3123(02)00133-5
Mustaffa, N., Ismail, Z., Tasir, Z., & Said, M. N. H. M. (2016). The impacts of implementing problem-based learning (PBL) in mathematics: A review of literature. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 6(12), 490-503. http://dx.doi.org/10.6007/IJARBSS/v6-i12/2513
Napitupulu, E.E., Suryadi, D., & Kusumah, Y.S. (2016). Cultivating Upper Secondary Students’ Mathematical Reasoning -Ability and Attitude towards Mathematics through Problem-Based Learning. Journal on Mathematics Education, 7(2), 117-128 https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.7.2.3542.117-128
Nurin, N. S., Junaedi, I., & Cahyono, A. N. (2024). Learning numeracy around school environment supported by mobile math trails using problem-based learning model. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(3), 485-498. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i3.pp485-498
Oberlander, J., & Talbert-Johnson, C. (2004). Using technology to support problem-based learning. Action in teacher education, 25(4), 48-57. https://doi.org/10.1080/01626620.2004.10648296
Plomp, T., & Nieveen, N. (2013). Educational design research: An introduction. Educational design research. Enschede, The Netherlands: SLO
Putri, R. I. I., & Zulkardi. (2017). Fraction in shot-put: A learning trajectory. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1868, 050005. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995132
Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, & Riskanita, A. D. (2022). Students’ problem-solving ability in solving algebra tasks using the context of Palembang. Journal on Mathematics Education, 13(3), 549–564. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v13i3.pp549-564
Risdiyanti, I., & Prahmana, R. C. I. (2021). Designing learning trajectory of set through the indonesian shadow puppets and mahabharata stories. Infinity Journal, 10(2), 331-348. http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9093-5851
Sari, A., & Putri, R. I. I. (2021). Inductive reasoning ability of students using the Palembang songket fabric context in rotational learning in grade IX. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(1), 57–72. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.14304.57-72
Schoen, R. C., Rhoads, C., Perez, A., Jacobbe, T., & Li, L. (2025). Improving the teaching and learning of statistics. Learning and Instruction, 95, 102018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2024.102018
Taleb, Z., Ahmadi, A., & Musavi, M. (2015). The effect of m-learning on mathematics learning. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 171, 83-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.092
Ulfah, A. S., Yerizon, Y., & Arnawa, I. M. (2020). Preliminary research of mathematics learning device development based on Realistic Mathematics Education (RME). Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1554, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1554/1/012027