Main Article Content
Abstract
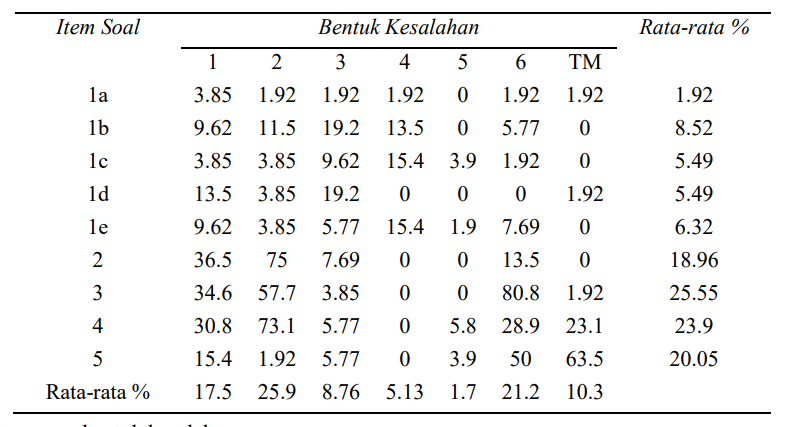
In the educational world, the challenge of some universities is to create graduates who are competent in their field. One of the competencies required of graduates of Mathematics Education in STKIP Singkawang is skills in solving math problems correctly and appropriately. According to reality on the ground, there are many students turned out to have any errors in problem-solving algebra. This is because the material Algebra is one area of Mathematics, that is considered difficult. The purpose of this study is to describe and identify errors Algebra students work on the problems and the factors that affect the mistakes made. The results obtained student errors relating to the algebraic concepts of 17.5%, the error associated with the error count of 25.9%, an error in the algorithm deviation of 8.76%, a typing error and the use of the mark by 5.13%, to answer any error of 1.7%, a matter which was not finished at 21.2% and answer questions that are not answered at all by 10.3%. Internal factors affecting the students make mistakes in solving algebra include the physical and psychological factors, but external factors include family and community environment factors.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2018 Rosmaiyadi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Arikunto, S.(2013). Dasar-dasar evaluasi pendidikan. Jakarta : PT Bumi Aksara.
- Ashlock, R.B. (2006). Error patterns in computation 9th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill. Abdurrahman, M. (1999). Pendidikan bagi anak berkesulitan belajar. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
- Astuti, E.P. (2006). Identifikasi kesalahan menyelesaikan kesalahan kalkulus lanjut mahasiswa program studi pendidikan matematika Universitas Muhammadiyah Purworejo. Jurnal Universitas Muhammadiyah Purworejo.
- Dimyati, & Mudjiono. (2006). Belajar dan pembelajaran. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta. Djaali, H. (2007). Psikologi pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
- Hamalik, O. (2006). Pendidikan guru berdasarkan pendekatan kompetensi. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara. Harun, R. (2007). Metode penelitian kualitatif untuk pelatihan. Bandung: Mandar Maju.
- Moleong, L.J. (2007). Metode penelitian kualitatif. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
- Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan No 58 Tahun 2014. (2014). Jakarta: Kemendikbud Republik Indonesia.
- Pramudjono. (2007). Aljabar. Samarinda: FKIP Universitas Mulawarman.
- Purwanto, N. (2007). Ilmu pendidikan teoritis dan praktis. Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosdakarya. Patton, M. (2006). Metode evaluasi kualitatif. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
- Sanjaya, W.W. (2007). Strategi pembelajaran berorientasi standar proses pendidikan. Jakarta: Kencana.
- Sardiman, A.M. (2007). Interaksi dan motivasi belajar mengajar. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada. Slamet, H.W. (2004). Problematika pengajaran kalkulus-1 mahasiswa semester awal. Jurnal Kajian Penelitian Pendidikan Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta, 16 (1).
- Soedjadi, R. (2000). Kiat pendidikan matematika di Indonesia. Jakarta : Depdiknas Sudiyono, A. (2006). Pengantar evaluasi pendidikan. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada.
- Suhartin, R.I. (1989). Mengatasi kesulitan-kesulitan dalam pendidikan anak. Jakarta: PT. BPK Gunung Mulia.
- Sugiyono.(2012). Metode penelitian kuantitatif kualitatif dan R & D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
- Syah, M. (2008). Psikologi pendidikan dengan pendekatn baru (Edisi Revisi). Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosdakarya.
References
Arikunto, S.(2013). Dasar-dasar evaluasi pendidikan. Jakarta : PT Bumi Aksara.
Ashlock, R.B. (2006). Error patterns in computation 9th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill. Abdurrahman, M. (1999). Pendidikan bagi anak berkesulitan belajar. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Astuti, E.P. (2006). Identifikasi kesalahan menyelesaikan kesalahan kalkulus lanjut mahasiswa program studi pendidikan matematika Universitas Muhammadiyah Purworejo. Jurnal Universitas Muhammadiyah Purworejo.
Dimyati, & Mudjiono. (2006). Belajar dan pembelajaran. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta. Djaali, H. (2007). Psikologi pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Hamalik, O. (2006). Pendidikan guru berdasarkan pendekatan kompetensi. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara. Harun, R. (2007). Metode penelitian kualitatif untuk pelatihan. Bandung: Mandar Maju.
Moleong, L.J. (2007). Metode penelitian kualitatif. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan No 58 Tahun 2014. (2014). Jakarta: Kemendikbud Republik Indonesia.
Pramudjono. (2007). Aljabar. Samarinda: FKIP Universitas Mulawarman.
Purwanto, N. (2007). Ilmu pendidikan teoritis dan praktis. Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosdakarya. Patton, M. (2006). Metode evaluasi kualitatif. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Sanjaya, W.W. (2007). Strategi pembelajaran berorientasi standar proses pendidikan. Jakarta: Kencana.
Sardiman, A.M. (2007). Interaksi dan motivasi belajar mengajar. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada. Slamet, H.W. (2004). Problematika pengajaran kalkulus-1 mahasiswa semester awal. Jurnal Kajian Penelitian Pendidikan Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta, 16 (1).
Soedjadi, R. (2000). Kiat pendidikan matematika di Indonesia. Jakarta : Depdiknas Sudiyono, A. (2006). Pengantar evaluasi pendidikan. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada.
Suhartin, R.I. (1989). Mengatasi kesulitan-kesulitan dalam pendidikan anak. Jakarta: PT. BPK Gunung Mulia.
Sugiyono.(2012). Metode penelitian kuantitatif kualitatif dan R & D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Syah, M. (2008). Psikologi pendidikan dengan pendekatn baru (Edisi Revisi). Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosdakarya.