Main Article Content
Abstract
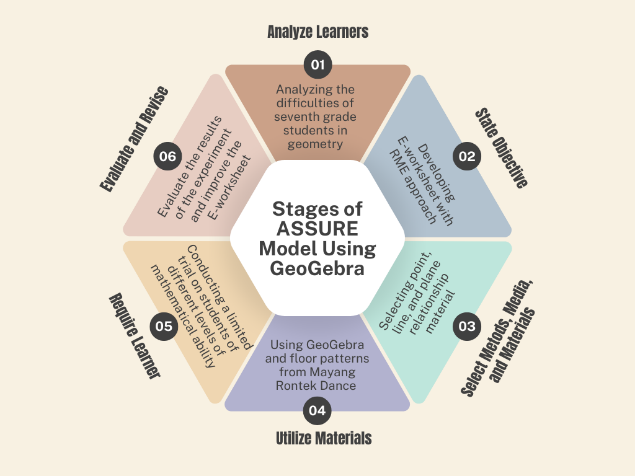
The e-worksheet is an interactive tool that allows students to access questions and explore information electronically, supporting their understanding of the concepts being studied. This study aims to develop a valid and effective e-worksheet based on the Ethno-Pendidikan Matematika Realistik Indonesia (PMRI) approach, incorporating the context of the Mayang Rontek Dance, to assist students in learning geometry. The research followed the ASSURE model, which includes six stages: analyzing students' needs, defining objectives, selecting appropriate media and materials, engaging learners, and evaluating and revising the developed e-worksheet. The e-worksheet underwent validation by three experts using Aiken’s analysis technique. Limited trials were conducted with six junior high school students, followed by field trials with twenty-nine students. The results revealed that the e-worksheet was valid, with Aiken indices ranging from 0.59 to 0.89. Statistical analysis using the Wilcoxon test on pre-test and post-test scores successfully rejected the null hypothesis, indicating that the e-worksheet effectively improved students' test scores. Furthermore, the practicality test yielded a score of 84.97%, demonstrating the e-worksheet's high level of practicality. Thus, the developed e-worksheet has been validated as both effective and practical in enhancing students’ understanding of geometry. The integration of the Ethno-PMRI approach and GeoGebra is expected to further enrich students' comprehension of mathematical concepts and their connection to local culture.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2025 Taszkia Aulia Putri, Nurul Fadilah, Tika Anjasari, Yurizka Melia Sari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Aisyah, F., Lestari, A. A. P., Supriyanto, M. A., & Nursyahidah, F. (2022). Exploration of Sam Poo Kong Building Heritage as Starting Point in Geometric Transformation Course. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(1), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.13073.15-28
- Altin, M. (2021). Evaluation of the Effectiveness of English Instruction based on ASSURE Model. E-International Journal of Educational Research, 12, 195–211. https://doi.org/10.19160/e-ijer.1018149
- DeCastellarnau, A. (2018). A classification of response scale characteristics that affect data quality: a literature review. Quality and Quantity, 52(4), 1523–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-017-0533-4
- Deda, Y. N., & Maifa, T. (2021). Development of Student Worksheets Using the Context of Local Wisdom on Integers and Fractions. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 15(1), 71–82. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.15.1.12824.71-82
- Divayana, D. G. H., Adiarta, A., & Sudirtha, I. G. (2019). The Content Validity of Digital Test Items for Evaluation Courses Based on Superitem- Wondershare Using Aiken ’ s Calculation The Content Validity of Digital Test Items for Evaluation Courses Based on Superitem - Wondershare Using Aiken ’ s Calculation. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1417/1/012040
- Febrian, F., & Astuti, P. (2018). The RME principles on geometry learning with focus of transformation reasoning through exploration on Malay woven motif. Journal of Turkish Science Education, 15(Special Issue), 33–41. https://doi.org/10.12973/tused.10254a
- Fiandini, M., Nandiyanto, A. B. D., Al Husaeni, D. F., Al Husaeni, D. N., & Mushiban, M. (2024). How to Calculate Statistics for Significant Difference Test Using SPSS: Understanding Students Comprehension on the Concept of Steam Engines as Power Plant. Indonesian Journal of Science and Technology, 9(1), 45–108. https://doi.org/10.17509/ijost.v9i1.64035
- Fredriksen, H. (2021). Exploring Realistic Mathematics Education in a Flipped Classroom Context at the Tertiary Level. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 19(2), 377–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-020-10053-1
- Haryanti, M. D., Herman, T., & Prabawanto, S. (2019). Analysis of students’ error in solving mathematical word problems in geometry. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1157(4). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1157/4/042084
- Hasmawaty, H., Syam, H., & Saman, A. (2020). Validity, Practicality, and Effectiveness: The Last Step in Development of Entrepreneurship Education Based Role-Playing for Kindergarten. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(12B), 8092–8101. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.082611
- Joshi, A., Kale, S., Chandel, S., & Pal, D. (2015). Likert Scale: Explored and Explained. British Journal of Applied Science & Technology, 7(4), 396–403. https://doi.org/10.9734/bjast/2015/14975
- Kang, H. (2021). Sample size determination and power analysis using the G*Power software. Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions, 18, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3352/JEEHP.2021.18.17
- Kim, D., & Downey, S. (2016). Examining the Use of the ASSURE Model by K–12 Teachers. Computers in the Schools, 33(3), 153–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/07380569.2016.1203208
- Maruti, E. S., Cahyono, B. E. H., Kurniawati, R. P., & Hanif, M. (2024). Do Javanese textbooks convey relevant material? Evidence of readability and value of learning outcomes. Preventing School Failure, 68(2), 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/1045988X.2023.2181299
- Mirna, M. (2018). Errors Analysis of Students in Mathematics Department to Learn Plane Geometry. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 335(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/335/1/012116
- Murtafiah, W., Wardani, Y. N., Darmadi, D., & Widodo, S. A. (2024). Profile of open-start problem-solving with context Sarangan Lake viewed students’ learning styles in junior high school. Journal of Education and Learning, 18(2), 448–461. https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v18i2.21051
- Nindiasari, H., Pranata, M. F., Sukirwan, Sugiman, Fathurrohman, M., Ruhimat, A., & Yuhana, Y. (2024). the Use of Augmented Reality To Improve Students’ Geometry Concept Problem-Solving Skills Through the Steam Approach. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 119–138. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p119-138
- Nuraida, E. M., & Putri, R. I. I. (2019). the Context of Archipelago Traditional Cake To Explore Students’ Understanding in Integers Division Class Vii. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(1), 91–100. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.1.7400.91-100
- Prahmana, R. C. I. (2022). Ethno-Realistic Mathematics Education: The promising learning approach in the city of culture. Springer Nature Social Sciences, 2(12), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-022-00571-w
- Prahmana, R. C. I., & D’Ambrosio, U. (2020). Learning geometry and values from patterns: Ethnomathematics on the batik patterns of yogyakarta, indonesia. Journal on Mathematics Education, 11(3), 439–456. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.11.3.12949.439-456
- Putra, A. K., Al Khalidy, D., Handoyo, B., & Van Thang, H. (2023). Construction of Immersive Experiences: Development of Virtual Reality Technology to Facilitate Physical Geography Learning. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (IJET), 18(19), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v18i19.40859
- Putri, R. I. I., Dolk, M., & Zulkardi. (2015). Professional Development of PMRI Teachers for Introduction Social Norm. Journal on Mathematics Education, 6(1), 11–19. https://doi.org/dx.doi.org/10.22342/jme.61.11
- Rawani, D., Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, & Susanti, E. (2023). RME-based local instructional theory for translation and reflection using of South Sumatra dance context. Journal on Mathematics Education, 14(3), 545–562. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v14i3.pp545-562
- Rosa, M., D’Ambrosio, U., Orey, D. C., Shirley, L., Alangui, W. V., Palhares, P., & Gavarrete, M. E. (2016). Current and Future Perspectives of Ethnomathematics as a Program (G. Kaiser, Ed.). ICME-13 Topical Surveys. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-30120-4_1
- Sari, A., & Putri, R. I. I. (2021). Inductive Reasoning Ability of Students Using the Palembang Songket Fabric Context in Rotational Learning in Grade IX. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(1), 57–72. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.14304.57-72
- Sari, D. S., Widiyawati, Y., Nurwahidah, I., Masykuri, M., & Budiyanto, C. W. (2021). The Development of E-Worksheet Based on Project to Promote Student’s Creative Thinking and Digital Literacy Skills. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Research, Implementation, and Education of Mathematics and Sciences (ICRIEMS 2020), 528(Icriems 2020), 647–654. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.210305.094
- Sari, Y. M., Fiangga, S., Milla, Y. I. El, & Puspaningtyas, N. D. (2023). Exploring students’ proportional reasoning in solving guided-unguided area conservation problem: A case of Indonesian students. Journal on Mathematics Education, 14(2), 375–394. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v14i2.pp375-394
- Sharma, S. (2024). Exploring children’s negotiation of meanings about “D” in 2D and 3D shapes in a year 5/6 New Zealand primary classroom. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 36(2), 259–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00443-3
- Sudirman, Javier, G., Rodríguez-Nieto, C. A., & Son, A. L. (2024). Exploring Junior High School Students’ Geometry Self-Efficacy In Solving 3d Geometry Problems Through 5e Instructional Model Intervention: A Grounded Theory Study. Infinity: Journal of Mathematics Education, 13(1), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p215-232
- Sutama, H. J., Narimo, S., Ishartono, N., & Sari, D. P. (2021). The development of student worksheets based on higher order thinking skill for mathematics learning in junior high school. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1776(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1776/1/012032
- Syafitri, R. A., & Tressyalina. (2020). The Importance of the Student Worksheets of Electronic (E-LKPD) Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) in Learning to Write Description Text during Pandemic COVID-19. 485(Iclle), 284–287. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.201109.048
- Ulusoy, F., & Çakıroğlu, E. (2021). Exploring prospective teachers’ noticing of students’ understanding through micro-case videos. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 24(3), 253–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-020-09457-1
- Widyaningrum, R., & Prihastari, E. B. (2020). Student worksheet based on Surakarta’s local wisdom in primary school: A preliminary research. International Journal of Science and Applied Science: Conference Series, 4(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.20961/ijsascs.v4i1.49458
- Yanto, D. T. P., Ganefri, Sukardi, Yanto, J. P., Samala, A. D., Dewi, I. P., Kurani, R., Setiawan, H., & Kabatiah, M. (2024). Innovative Laboratory Learning: A Study Evaluating the Practicality of Integrated E-Worksheets with Augmented Reality in Electrical Machines Course. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 14(7), 996–1005. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijiet.2024.14.7.2127
- Zulkardi. (2002). Developing A Learning Environment on Realistic Mathematics Education for Indonesian Students Teachers. University of Twente. https://research.utwente.nl/en/publications/developing-a-learning-environment-on-realistic-mathematics-educat
- Zulkardi., Putri, R. I. I., & Wijaya, A. (2020). Two Decades of Realistic Mathematics Education in Indonesia. In International Reflection on the Netherland Didactic of Mathematics (pp. 325–340). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20223-1_18
References
Aisyah, F., Lestari, A. A. P., Supriyanto, M. A., & Nursyahidah, F. (2022). Exploration of Sam Poo Kong Building Heritage as Starting Point in Geometric Transformation Course. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(1), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.13073.15-28
Altin, M. (2021). Evaluation of the Effectiveness of English Instruction based on ASSURE Model. E-International Journal of Educational Research, 12, 195–211. https://doi.org/10.19160/e-ijer.1018149
DeCastellarnau, A. (2018). A classification of response scale characteristics that affect data quality: a literature review. Quality and Quantity, 52(4), 1523–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-017-0533-4
Deda, Y. N., & Maifa, T. (2021). Development of Student Worksheets Using the Context of Local Wisdom on Integers and Fractions. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 15(1), 71–82. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.15.1.12824.71-82
Divayana, D. G. H., Adiarta, A., & Sudirtha, I. G. (2019). The Content Validity of Digital Test Items for Evaluation Courses Based on Superitem- Wondershare Using Aiken ’ s Calculation The Content Validity of Digital Test Items for Evaluation Courses Based on Superitem - Wondershare Using Aiken ’ s Calculation. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1417/1/012040
Febrian, F., & Astuti, P. (2018). The RME principles on geometry learning with focus of transformation reasoning through exploration on Malay woven motif. Journal of Turkish Science Education, 15(Special Issue), 33–41. https://doi.org/10.12973/tused.10254a
Fiandini, M., Nandiyanto, A. B. D., Al Husaeni, D. F., Al Husaeni, D. N., & Mushiban, M. (2024). How to Calculate Statistics for Significant Difference Test Using SPSS: Understanding Students Comprehension on the Concept of Steam Engines as Power Plant. Indonesian Journal of Science and Technology, 9(1), 45–108. https://doi.org/10.17509/ijost.v9i1.64035
Fredriksen, H. (2021). Exploring Realistic Mathematics Education in a Flipped Classroom Context at the Tertiary Level. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 19(2), 377–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-020-10053-1
Haryanti, M. D., Herman, T., & Prabawanto, S. (2019). Analysis of students’ error in solving mathematical word problems in geometry. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1157(4). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1157/4/042084
Hasmawaty, H., Syam, H., & Saman, A. (2020). Validity, Practicality, and Effectiveness: The Last Step in Development of Entrepreneurship Education Based Role-Playing for Kindergarten. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(12B), 8092–8101. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.082611
Joshi, A., Kale, S., Chandel, S., & Pal, D. (2015). Likert Scale: Explored and Explained. British Journal of Applied Science & Technology, 7(4), 396–403. https://doi.org/10.9734/bjast/2015/14975
Kang, H. (2021). Sample size determination and power analysis using the G*Power software. Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions, 18, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3352/JEEHP.2021.18.17
Kim, D., & Downey, S. (2016). Examining the Use of the ASSURE Model by K–12 Teachers. Computers in the Schools, 33(3), 153–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/07380569.2016.1203208
Maruti, E. S., Cahyono, B. E. H., Kurniawati, R. P., & Hanif, M. (2024). Do Javanese textbooks convey relevant material? Evidence of readability and value of learning outcomes. Preventing School Failure, 68(2), 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/1045988X.2023.2181299
Mirna, M. (2018). Errors Analysis of Students in Mathematics Department to Learn Plane Geometry. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 335(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/335/1/012116
Murtafiah, W., Wardani, Y. N., Darmadi, D., & Widodo, S. A. (2024). Profile of open-start problem-solving with context Sarangan Lake viewed students’ learning styles in junior high school. Journal of Education and Learning, 18(2), 448–461. https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v18i2.21051
Nindiasari, H., Pranata, M. F., Sukirwan, Sugiman, Fathurrohman, M., Ruhimat, A., & Yuhana, Y. (2024). the Use of Augmented Reality To Improve Students’ Geometry Concept Problem-Solving Skills Through the Steam Approach. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 119–138. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p119-138
Nuraida, E. M., & Putri, R. I. I. (2019). the Context of Archipelago Traditional Cake To Explore Students’ Understanding in Integers Division Class Vii. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(1), 91–100. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.1.7400.91-100
Prahmana, R. C. I. (2022). Ethno-Realistic Mathematics Education: The promising learning approach in the city of culture. Springer Nature Social Sciences, 2(12), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-022-00571-w
Prahmana, R. C. I., & D’Ambrosio, U. (2020). Learning geometry and values from patterns: Ethnomathematics on the batik patterns of yogyakarta, indonesia. Journal on Mathematics Education, 11(3), 439–456. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.11.3.12949.439-456
Putra, A. K., Al Khalidy, D., Handoyo, B., & Van Thang, H. (2023). Construction of Immersive Experiences: Development of Virtual Reality Technology to Facilitate Physical Geography Learning. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (IJET), 18(19), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v18i19.40859
Putri, R. I. I., Dolk, M., & Zulkardi. (2015). Professional Development of PMRI Teachers for Introduction Social Norm. Journal on Mathematics Education, 6(1), 11–19. https://doi.org/dx.doi.org/10.22342/jme.61.11
Rawani, D., Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, & Susanti, E. (2023). RME-based local instructional theory for translation and reflection using of South Sumatra dance context. Journal on Mathematics Education, 14(3), 545–562. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v14i3.pp545-562
Rosa, M., D’Ambrosio, U., Orey, D. C., Shirley, L., Alangui, W. V., Palhares, P., & Gavarrete, M. E. (2016). Current and Future Perspectives of Ethnomathematics as a Program (G. Kaiser, Ed.). ICME-13 Topical Surveys. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-30120-4_1
Sari, A., & Putri, R. I. I. (2021). Inductive Reasoning Ability of Students Using the Palembang Songket Fabric Context in Rotational Learning in Grade IX. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(1), 57–72. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.14304.57-72
Sari, D. S., Widiyawati, Y., Nurwahidah, I., Masykuri, M., & Budiyanto, C. W. (2021). The Development of E-Worksheet Based on Project to Promote Student’s Creative Thinking and Digital Literacy Skills. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Research, Implementation, and Education of Mathematics and Sciences (ICRIEMS 2020), 528(Icriems 2020), 647–654. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.210305.094
Sari, Y. M., Fiangga, S., Milla, Y. I. El, & Puspaningtyas, N. D. (2023). Exploring students’ proportional reasoning in solving guided-unguided area conservation problem: A case of Indonesian students. Journal on Mathematics Education, 14(2), 375–394. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v14i2.pp375-394
Sharma, S. (2024). Exploring children’s negotiation of meanings about “D” in 2D and 3D shapes in a year 5/6 New Zealand primary classroom. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 36(2), 259–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00443-3
Sudirman, Javier, G., Rodríguez-Nieto, C. A., & Son, A. L. (2024). Exploring Junior High School Students’ Geometry Self-Efficacy In Solving 3d Geometry Problems Through 5e Instructional Model Intervention: A Grounded Theory Study. Infinity: Journal of Mathematics Education, 13(1), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p215-232
Sutama, H. J., Narimo, S., Ishartono, N., & Sari, D. P. (2021). The development of student worksheets based on higher order thinking skill for mathematics learning in junior high school. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1776(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1776/1/012032
Syafitri, R. A., & Tressyalina. (2020). The Importance of the Student Worksheets of Electronic (E-LKPD) Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) in Learning to Write Description Text during Pandemic COVID-19. 485(Iclle), 284–287. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.201109.048
Ulusoy, F., & Çakıroğlu, E. (2021). Exploring prospective teachers’ noticing of students’ understanding through micro-case videos. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 24(3), 253–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-020-09457-1
Widyaningrum, R., & Prihastari, E. B. (2020). Student worksheet based on Surakarta’s local wisdom in primary school: A preliminary research. International Journal of Science and Applied Science: Conference Series, 4(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.20961/ijsascs.v4i1.49458
Yanto, D. T. P., Ganefri, Sukardi, Yanto, J. P., Samala, A. D., Dewi, I. P., Kurani, R., Setiawan, H., & Kabatiah, M. (2024). Innovative Laboratory Learning: A Study Evaluating the Practicality of Integrated E-Worksheets with Augmented Reality in Electrical Machines Course. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 14(7), 996–1005. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijiet.2024.14.7.2127
Zulkardi. (2002). Developing A Learning Environment on Realistic Mathematics Education for Indonesian Students Teachers. University of Twente. https://research.utwente.nl/en/publications/developing-a-learning-environment-on-realistic-mathematics-educat
Zulkardi., Putri, R. I. I., & Wijaya, A. (2020). Two Decades of Realistic Mathematics Education in Indonesia. In International Reflection on the Netherland Didactic of Mathematics (pp. 325–340). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20223-1_18