Main Article Content
Abstract
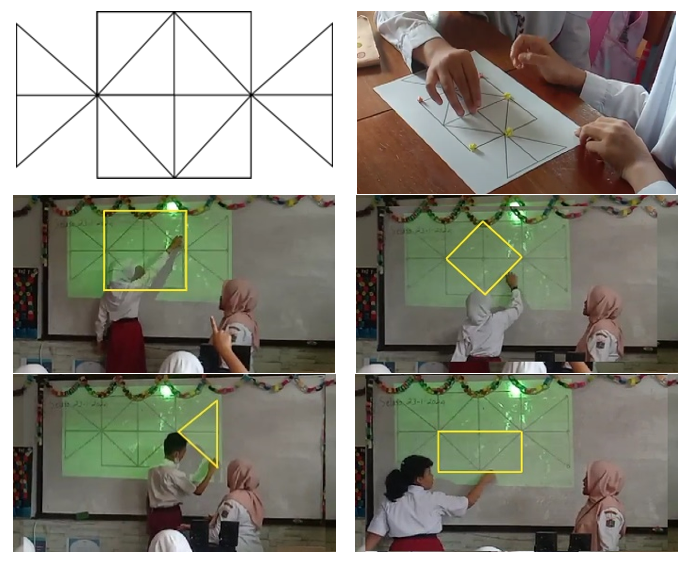
One of the demands of 21st century learning is critical thinking. However, nowadays, students' critical thinking skills are still relatively low, particularly in geometry. This research aims to explore students' critical thinking skills through the design of a series of lessons. Realistic Mathematics Education (RME) underlies the design and the context applied. This study was conducted in one of the elementary schools in Jakarta, involving 30 grade IV elementary school students as the research subjects. The method used in this research is descriptive qualitative with an educational ethnographic approach. Data collection techniques involved observation, interviews, and documentation. The results of this study indicate that the implementation of a traditional game-based learning design called Damdas 3 Batu can support students’ critical thinking skills. Through this game, students are able to comprehend the given problems, construct mathematical models adapted to the provided context, solve the problems, and ultimately derive conclusions from the obtained results. Therefore, Damdas 3 Batu can serve as a valuable instructional reference for teaching geometry concepts in elementary schools.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2024 PDF

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Abouelgheat, K. R. A. (2021). Learners’ mathematics proficiency levels on PISA 2018: A comparative study. International Journal of Instruction, 14(3), 393–416. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2021.14323a
- Arini, R., Rahayu, Y. S., & Erman, E. (2023). Profile of critical thinking results analyzed from facione indicators and gender of learners. IJORER : International Journal of Recent Educational Research, 4(4), 434–446. https://doi.org/10.46245/ijorer.v4i4.328
- Arseven, A. (2015). Mathematical modelling approach in mathematics education. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 3(12), 973–980. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2015.031204
- Arytunova, A., & Gykasyan, S. (2021). Development of logical thinking in primary school students in mathematics lessons. 8(2), 56–60. https://doi.org/10.52376/978-5-907419-23-0_056
- Chankseliani, M., Qoraboyev, I., & Gimranova, D. (2021). Higher education contributing to local, national, and global development: New empirical and conceptual insights. Higher Education, 81(1), 109–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-020-00565-8
- Code, W., Merchant, S., Maciejewski, W., Thomas, M., & Lo, J. (2016). The Mathematics attitudes and perceptions survey: An instrument to assess expert-like views and dispositions among undergraduate mathematics students. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 47(6), 917–937. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2015.1133854
- Facione, P. A. (1990). Critical thinking: A statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research Findings and Recommendations. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED315423.pdf
- Fauziah, A., Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, & Somakim. (2020). Developing PMRI learning environment through lesson study for pre-service primary school teacher. Journal on Mathematics Education, 11(2), 193–208. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.11.2.10914.193-208
- Güner, P., & Erbay, H. N. (2021). Metacognitive skills and problem- solving to cite this article : Metacognitive skills and problem-solving. International Journal of Research in Education and Science, 7(3), 715–734. https://www.ijres.net/index.php/ijres/article/view/1594
- Jaelani, A., Putri, R. I. I., & Hartono, Y. (2013). Students’ strategies of measuring time using traditional. Journal on Mathematics Education, 4(1), 29–40. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1078954
- Kek, M. Y. C. A., & Huijser, H. (2011). The power of problem-based learning in developing critical thinking skills: Preparing students for tomorrow’s digital futures in today’s classrooms. Higher Education Research and Development, 30(3), 329–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2010.501074
- Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. (2017). Panduan Penilaian oleh Pendidik dan Satuan Pendidikan Sekolah Menengah Pertama. Jakarta: Kementerian Pendidikan Dan Kebudayaan. http://repositori.kemdikbud.go.id/18051/1/1.
- Kirmizi, F. S., Saygi, C., & Yurdakal, I. H. (2015). Determine the relationship between the disposition of critical thinking and the perception about problem solving skills. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 191, 657–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.04.719
- Masfingatin, T., Murtafiah, W., & Maharani, S. (2020). Exploration of creative mathematical reasoning in solving geometric problems. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(2), 155–168. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.2.7654.155-168
- Masruroh, D. E. A., & Isnaini, N. (2022). The effect of the traditional board game “dam-daman” on the elderly cognitive functions at the elderly integrated health center, Pegongsoran, Pemalang District, Pemalang. Proceedings Series on Health & Medical Sciences, 2, 127–132. https://doi.org/10.30595/pshms.v2i.234
- Nieminen, J. H., & Atjonen, P. (2023). The assessment culture of mathematics in Finland: a student perspective. Research in Mathematics Education, 25(2), 243–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2022.2045626
- Nabavi, S. T., & Fossen, H. (2021). Fold geometry and folding – a review. Earth-Science Reviews, 222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103812
- Nursyahidah, F., Putri, R. I. I., & Somakim. (2013). Supporting first grade students’ understanding of addition up to 20 using traditional game. Journal on Mathematics Education, 4(2), 212–223. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.4.2.557.212-223
- Parker, J. M. (2018). Problematising ethnography and case study: Reflections on using ethnographic techniques and researcher positioning. Ethnography and Education, 13(1), 18–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/17457823.2016.1253028
- Puspitasari, N. A., Yanti, P. G., Sukardi, & Nofiyanti, F. (2020). The Education philosophy in sumatera traditional games: Recording islands in Indonesia to preserve culture. 477, 529–533. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.201017.117
- Rahma, R. A., Sucipto, Affriyenni, Y., & Widyaswari, M. (2021). Cybergogy as a digital media to facilitate the learning style of millennial college students. World Journal on Educational Technology: Current Issues, 13(2), 223–235. https://doi.org/10.18844/wjet.v13i2.5691
- Raj, A. B. (2017). Factors affecting difficulties in learning mathematics by mathematics learners. International Journal of Elementary Education, 6(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijeedu.20170602.11
- Runnalls, C., & Hong, D. S. (2020). “Well, they understand the concept of area”: Pre-service teachers’ responses to student area misconceptions. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 32(4), 629–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-019-00274-1
- Samo, D. D., Darhim, & Kartasasmita, B. G. (2018). Culture-based contextual learning to increase problem-solving ability of first year university student. Journal on Mathematics Education, 9(1), 81–93. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.1.4125.81-94
- Schooner, P., Nordlöf, C., Klasander, C., & Hallström, J. (2017). Design, system, value: The role of problem-solving and critical thinking capabilities in technology education, as perceived by teachers. Design and Technologyu Education: An International Journal , 22(3), 60–75. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1164329
- Setiana, D. S., Purwoko, R. Y., & Sugiman. (2021). The application of mathematics learning model to stimulate mathematical critical thinking skills of senior high school students. European Journal of Educational Research, 10(1), 509–523. https://doi.org/10.12973/EU-JER.10.1.509
- Simamora, R. E., Saragih, S., & Hasratuddin, H. (2018). Improving students’ mathematical problem solving ability and self-efficacy through guided discovery learning in local culture context. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(1), 61–72. https://doi.org/10.12973/iejme/3966
- Sumarni, W., & Kadarwati, S. (2020). Ethno-STEM project-based learning: Its impact to critical and creative thinking skills. Jurnal Pendidikan IPA Indonesia, 9(1), 11–21. https://doi.org/10.15294/jpii.v9i1.21754
- Van den Heuvel-Panhuizen, M., & Drijvers, P. (2020). Realistic Mathematics Education. In: Lerman, S. (eds.) Encyclopedia of Mathematics Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15789-0_170
- Verschaffel, L., Schukajlow, S., Star, J., & Van Dooren, W. (2020). Word problems in mathematics education: a survey. ZDM - Mathematics Education, 52(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-020-01130-4
References
Abouelgheat, K. R. A. (2021). Learners’ mathematics proficiency levels on PISA 2018: A comparative study. International Journal of Instruction, 14(3), 393–416. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2021.14323a
Arini, R., Rahayu, Y. S., & Erman, E. (2023). Profile of critical thinking results analyzed from facione indicators and gender of learners. IJORER : International Journal of Recent Educational Research, 4(4), 434–446. https://doi.org/10.46245/ijorer.v4i4.328
Arseven, A. (2015). Mathematical modelling approach in mathematics education. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 3(12), 973–980. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2015.031204
Arytunova, A., & Gykasyan, S. (2021). Development of logical thinking in primary school students in mathematics lessons. 8(2), 56–60. https://doi.org/10.52376/978-5-907419-23-0_056
Chankseliani, M., Qoraboyev, I., & Gimranova, D. (2021). Higher education contributing to local, national, and global development: New empirical and conceptual insights. Higher Education, 81(1), 109–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-020-00565-8
Code, W., Merchant, S., Maciejewski, W., Thomas, M., & Lo, J. (2016). The Mathematics attitudes and perceptions survey: An instrument to assess expert-like views and dispositions among undergraduate mathematics students. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 47(6), 917–937. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2015.1133854
Facione, P. A. (1990). Critical thinking: A statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research Findings and Recommendations. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED315423.pdf
Fauziah, A., Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, & Somakim. (2020). Developing PMRI learning environment through lesson study for pre-service primary school teacher. Journal on Mathematics Education, 11(2), 193–208. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.11.2.10914.193-208
Güner, P., & Erbay, H. N. (2021). Metacognitive skills and problem- solving to cite this article : Metacognitive skills and problem-solving. International Journal of Research in Education and Science, 7(3), 715–734. https://www.ijres.net/index.php/ijres/article/view/1594
Jaelani, A., Putri, R. I. I., & Hartono, Y. (2013). Students’ strategies of measuring time using traditional. Journal on Mathematics Education, 4(1), 29–40. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1078954
Kek, M. Y. C. A., & Huijser, H. (2011). The power of problem-based learning in developing critical thinking skills: Preparing students for tomorrow’s digital futures in today’s classrooms. Higher Education Research and Development, 30(3), 329–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2010.501074
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. (2017). Panduan Penilaian oleh Pendidik dan Satuan Pendidikan Sekolah Menengah Pertama. Jakarta: Kementerian Pendidikan Dan Kebudayaan. http://repositori.kemdikbud.go.id/18051/1/1.
Kirmizi, F. S., Saygi, C., & Yurdakal, I. H. (2015). Determine the relationship between the disposition of critical thinking and the perception about problem solving skills. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 191, 657–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.04.719
Masfingatin, T., Murtafiah, W., & Maharani, S. (2020). Exploration of creative mathematical reasoning in solving geometric problems. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(2), 155–168. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.2.7654.155-168
Masruroh, D. E. A., & Isnaini, N. (2022). The effect of the traditional board game “dam-daman” on the elderly cognitive functions at the elderly integrated health center, Pegongsoran, Pemalang District, Pemalang. Proceedings Series on Health & Medical Sciences, 2, 127–132. https://doi.org/10.30595/pshms.v2i.234
Nieminen, J. H., & Atjonen, P. (2023). The assessment culture of mathematics in Finland: a student perspective. Research in Mathematics Education, 25(2), 243–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2022.2045626
Nabavi, S. T., & Fossen, H. (2021). Fold geometry and folding – a review. Earth-Science Reviews, 222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103812
Nursyahidah, F., Putri, R. I. I., & Somakim. (2013). Supporting first grade students’ understanding of addition up to 20 using traditional game. Journal on Mathematics Education, 4(2), 212–223. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.4.2.557.212-223
Parker, J. M. (2018). Problematising ethnography and case study: Reflections on using ethnographic techniques and researcher positioning. Ethnography and Education, 13(1), 18–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/17457823.2016.1253028
Puspitasari, N. A., Yanti, P. G., Sukardi, & Nofiyanti, F. (2020). The Education philosophy in sumatera traditional games: Recording islands in Indonesia to preserve culture. 477, 529–533. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.201017.117
Rahma, R. A., Sucipto, Affriyenni, Y., & Widyaswari, M. (2021). Cybergogy as a digital media to facilitate the learning style of millennial college students. World Journal on Educational Technology: Current Issues, 13(2), 223–235. https://doi.org/10.18844/wjet.v13i2.5691
Raj, A. B. (2017). Factors affecting difficulties in learning mathematics by mathematics learners. International Journal of Elementary Education, 6(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijeedu.20170602.11
Runnalls, C., & Hong, D. S. (2020). “Well, they understand the concept of area”: Pre-service teachers’ responses to student area misconceptions. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 32(4), 629–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-019-00274-1
Samo, D. D., Darhim, & Kartasasmita, B. G. (2018). Culture-based contextual learning to increase problem-solving ability of first year university student. Journal on Mathematics Education, 9(1), 81–93. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.1.4125.81-94
Schooner, P., Nordlöf, C., Klasander, C., & Hallström, J. (2017). Design, system, value: The role of problem-solving and critical thinking capabilities in technology education, as perceived by teachers. Design and Technologyu Education: An International Journal , 22(3), 60–75. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1164329
Setiana, D. S., Purwoko, R. Y., & Sugiman. (2021). The application of mathematics learning model to stimulate mathematical critical thinking skills of senior high school students. European Journal of Educational Research, 10(1), 509–523. https://doi.org/10.12973/EU-JER.10.1.509
Simamora, R. E., Saragih, S., & Hasratuddin, H. (2018). Improving students’ mathematical problem solving ability and self-efficacy through guided discovery learning in local culture context. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(1), 61–72. https://doi.org/10.12973/iejme/3966
Sumarni, W., & Kadarwati, S. (2020). Ethno-STEM project-based learning: Its impact to critical and creative thinking skills. Jurnal Pendidikan IPA Indonesia, 9(1), 11–21. https://doi.org/10.15294/jpii.v9i1.21754
Van den Heuvel-Panhuizen, M., & Drijvers, P. (2020). Realistic Mathematics Education. In: Lerman, S. (eds.) Encyclopedia of Mathematics Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15789-0_170
Verschaffel, L., Schukajlow, S., Star, J., & Van Dooren, W. (2020). Word problems in mathematics education: a survey. ZDM - Mathematics Education, 52(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-020-01130-4