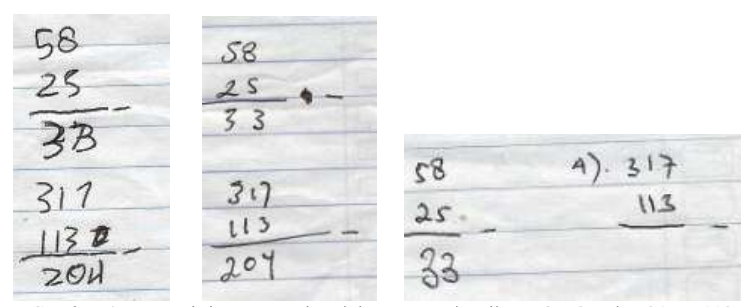Main Article Content
Abstract
The current research intends to both identify students’ strategies and clarify the level of students’ number sense
expression of primary students in solving problems relating to addition, subtraction, and multiplication of integers. This is a qualitative research. Five respondents are involved which are randomly taken from a primary school in Lombok Island. The data are collected through test. Meanwhile, data analysis utilize three indicators of number senses in order to answer two main research questions. The findings indicate that, firstly, the strategies used by the students to solve problems relating to addition, subtraction, and multiplication are homogenous, routine and standardized which are algorithm or procedure oriented, such as column addition, column subtraction, and column multiplication, respectively. Secondly, according to the four level of number sense expressions ─such as ‘not yet evident’, emerging, expressing, and excelling─, the findings indicate that the students’ level of number sense expression is categorized as ‘not yet evident’, which is the lowest level of the four level.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2018 Susilahudin Putrawangsa, Uswatun Hasanah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Bobis, J. (1991). The effect of instruction on the development of computation estimation strategies. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 3, 7-29.
- Case, R. & Sowder, J. (1990). The development of computational estimation: A neoPiagetian analysis. Cognition and Instruction, 7, 79-104.
- Cobb, P., Wood, T ., Yackel, E., Nicholls, J., Wheatley, G., Trigatti, B., & Perlwitz, M., (1991). Assessment of a problem-centred second-grade mathematics project. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 22, 3-29.
- Dehaene, S. (2011). The number sense: how the mind creates mathematics. Noe York: Oxford University Press.
- Devlin, K. (2017). Number sense: the most important mathematical concept in 21st Century K-12 education. HUFFPOST, (online (http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/number-sense-the- most-important-mathematical-concept_us_58695887e4b068764965c2e0).
- Fauzan, A. (2002). Applying Realistic Mathematics Education (RME) in Teaching Geometry in Indonesian Primary Schools. Doctoral Dissertation. The Netherlands: University of Twente.
- Fischer , F. (1990). A part-part-whole curriculum for teaching number to kindergarten. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 21, 207-215.
- Fosnot, C.T., & Dolk, M., (2001). Young Mathematician at Work: Constructing Number sense, addition, and substraction. Porstmouth, NH: Heinemann.
- Freudenthal, H. (1991). Revisiting mathematics education. The Netherlands, Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
- Hope, J., & Sherril, J. (1987). Characteristics of unskilled and skilled mental calculators. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 18, 98-1 1 1.
- NCTM. (2000). Principles and Standars for School Mathematics. Reston, VA: NCTM
- Neergaard, L. (2013). Early Number sense Plays Role in Later Math Skills. ABC News, (online), (http://www.abc2news.com/news/health/early-number-sense-plays-role-in-later-math-skills).
- Putrawangsa, S. (2013). Educational Design Research: Developing Students’ Understanding of The Multiplication Strategy in Area Measurement. Master Thesis. Surabaya: Universitas Negeri Surabaya.
- Putrawangsa, S. (2015). Students’ prior understanding of area. Beta Jurnal Tadris Matematika, 8 (2), 113 – 126.
- Paulos, J.A. (1988). Innumeracy: Mathematical illiteracy and its consequences. New York: Vintage.
- Reys, Robert E., and Nobuhiko Nohda, eds. (1994). Computational alternatives for the twenty-first century: cross-cultural perspectives from Japan and the United States. Reston, Va: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics.
- Ross, S. (1989). Parts, wholes, and place value: A developmental view. Arithmetic Teacher, 36, 47-51.
- Sowder, J.T. (1992). Making sense of numbers in school mathematics. In Analysis of Arithmetic for Mathematics Teaching, edited by Gaea Leinhardt, Ralph Putman, and Rosemary A. Hattrup, pp. 1–51. Hillsdale, N.J: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Trafton, P. (1992). Using number sense to develop mental computation and computational estimation. In C. Irons (Ed.) Challenging Children to Think when they Compute . (pp. 78-92). Brisbane: Centre for Mathematics and Science Education, Queensland University of Technology.
References
Bobis, J. (1991). The effect of instruction on the development of computation estimation strategies. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 3, 7-29.
Case, R. & Sowder, J. (1990). The development of computational estimation: A neoPiagetian analysis. Cognition and Instruction, 7, 79-104.
Cobb, P., Wood, T ., Yackel, E., Nicholls, J., Wheatley, G., Trigatti, B., & Perlwitz, M., (1991). Assessment of a problem-centred second-grade mathematics project. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 22, 3-29.
Dehaene, S. (2011). The number sense: how the mind creates mathematics. Noe York: Oxford University Press.
Devlin, K. (2017). Number sense: the most important mathematical concept in 21st Century K-12 education. HUFFPOST, (online (http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/number-sense-the- most-important-mathematical-concept_us_58695887e4b068764965c2e0).
Fauzan, A. (2002). Applying Realistic Mathematics Education (RME) in Teaching Geometry in Indonesian Primary Schools. Doctoral Dissertation. The Netherlands: University of Twente.
Fischer , F. (1990). A part-part-whole curriculum for teaching number to kindergarten. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 21, 207-215.
Fosnot, C.T., & Dolk, M., (2001). Young Mathematician at Work: Constructing Number sense, addition, and substraction. Porstmouth, NH: Heinemann.
Freudenthal, H. (1991). Revisiting mathematics education. The Netherlands, Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Hope, J., & Sherril, J. (1987). Characteristics of unskilled and skilled mental calculators. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 18, 98-1 1 1.
NCTM. (2000). Principles and Standars for School Mathematics. Reston, VA: NCTM
Neergaard, L. (2013). Early Number sense Plays Role in Later Math Skills. ABC News, (online), (http://www.abc2news.com/news/health/early-number-sense-plays-role-in-later-math-skills).
Putrawangsa, S. (2013). Educational Design Research: Developing Students’ Understanding of The Multiplication Strategy in Area Measurement. Master Thesis. Surabaya: Universitas Negeri Surabaya.
Putrawangsa, S. (2015). Students’ prior understanding of area. Beta Jurnal Tadris Matematika, 8 (2), 113 – 126.
Paulos, J.A. (1988). Innumeracy: Mathematical illiteracy and its consequences. New York: Vintage.
Reys, Robert E., and Nobuhiko Nohda, eds. (1994). Computational alternatives for the twenty-first century: cross-cultural perspectives from Japan and the United States. Reston, Va: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics.
Ross, S. (1989). Parts, wholes, and place value: A developmental view. Arithmetic Teacher, 36, 47-51.
Sowder, J.T. (1992). Making sense of numbers in school mathematics. In Analysis of Arithmetic for Mathematics Teaching, edited by Gaea Leinhardt, Ralph Putman, and Rosemary A. Hattrup, pp. 1–51. Hillsdale, N.J: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Trafton, P. (1992). Using number sense to develop mental computation and computational estimation. In C. Irons (Ed.) Challenging Children to Think when they Compute . (pp. 78-92). Brisbane: Centre for Mathematics and Science Education, Queensland University of Technology.