Main Article Content
Abstract
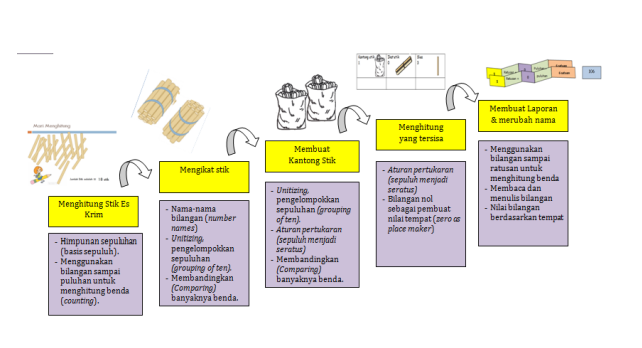
Understanding the concept of place value is very important for students in mastering the further mathematical concepts. However, the numbers of studies have shown that, students understanding of place value concepts are still problematic, because the place value learning experience in the classroom less meaningful where the learning is directly exposed to master the number of algorithms. In fact, should the place value learning should be emphasized to the students real experience with concrete objects to reinvent important concepts in place value. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the role place value learning trajectory that have been developed through PMRI approach by using video animation toward student’s understanding of place value concept in second grade primary school. To achieve these aims, this study using design research (Akker model), where the research include three phases preparing for the experiment, Experiment in the classroom, and Retrospective analysis. This discussion focuses only Retrospective analysis to explain the role of learning trajectory developed towards the understanding of the place value concept. The study involved 15 second gare students of SDN 19 in Banda Aceh. Teaching experiment results showed that the learning trajectory that was developed give students the opportunity to reinvent and understand the concept of place value.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2017 Rita Novita, Mulia Putra

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Andreasen, Janet.B. (2006). Classroom Mathematical Practices In A Preservice Elementary Mathematics Education Course Using An Instructional Sequence Related To Place Value And Operations. Published Disertasi. Department of Teaching and Learning Principles. University of Central Florida, Florida.
- Akker, J.V.d., Gravemeijer, K., McKenney, S., and Nieveen, N. (2006). EducationDesign Research. London: Routledge Taylor and Francis Group.
- Aksoy, G. (2012). The Effects of Animation Technique on the 7th Grade Science and Technology Course. Jurnal of Scientific Research. Vol.3, pp: 304-308, (Online), (http://www.SciRP.org/jornal/cc), diakses 30 Maret 2015.
- Aljupri. (2008). Design Research on Computational Estimation for Grade Five Primary School Students in Indonesia. Prosiding KNM XIV Palembang. Palembang: Sriwijaya University.
- Ashlock, R. B. 1994. Error Patterns in Computation. (6th ed). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Freudenthal, H. (1991). Revisiting Mathematics Education. China Lecture. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
- Garlikov. 2004. The Concep and Teaching of Place Value, (Online), (http://www.garlikov.com/PlaceValue.h tml), diakses 26 Maret 2015.
- Maria, G. 2011. Artacts and utilization schemes in mathematics teacher education: place value in early childhood education. J Math Teacher Educ (2011), DOI 10.007.
- Maria, V & Becker. 1997. Children’s Developing Understanding of Place Value: SemioticAspets. Cognition and Instruction, 15(2), 265-286. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Negoro, S.T. & Harahap, B. 1983. Ensiklopedia Matematika. Jakarta: Ghalia Indonesia.
- Novita, R. & Putra, M. 2012. Pemahaman Konsep Nilai Tempat dalam Mendukung Siswa Menyelesaikan Penjumlahan Bilangan Tiga Angka. Prosiding seminar nasional I, pp 183-192. Banda Aceh: Universitas Syiah Kuala
- Payne, J. N. & Huinker, D. M. 1993. Early Number and Numeration; dalam Jensen, R.J. (Ed.), Reasearch Ideas for the Classroom: Early Childhood Mathematics. (hlm. 43—70). New York: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics Research Interpretation Project/Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Prahmana, R.C.I. (2010). Permainan “Tepuk Bergilir” yang Berorientasi Konstruktivisme dalam Pembelajaran Konsep KPK Siswa Kelas IV A di SD N 21 Palembang. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika Volume 4 No. 2, pp. 61-69. Palembang: Universitas Sriwijaya
- Reys, R. E., Suydam, M. N., Lindquist, M. M., & Smith, N. L. 1984. Helping Children Learn Mathematics. (5th ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
- Seputra, T. MHT & Amin, S. M. 1994. Matematika 1b: Mari Berhitung untuk Sekolah Dasar Kelas 1 Cawu 2. Jakarta: Depdikbud-Balai Pustaka.
- Thomson. 2000. Teaching Place Value in UK: Time for Reapracial?. Educational Review. Vol 52, No 3, 2000. Department of Education, UK.
- Zulkardi. (2002). Developing A Learning Environment on Realistic Mathematics Education for Indonesian Student Teachers. Published Dissertation. Enschede: Universityof Twente.
References
Andreasen, Janet.B. (2006). Classroom Mathematical Practices In A Preservice Elementary Mathematics Education Course Using An Instructional Sequence Related To Place Value And Operations. Published Disertasi. Department of Teaching and Learning Principles. University of Central Florida, Florida.
Akker, J.V.d., Gravemeijer, K., McKenney, S., and Nieveen, N. (2006). EducationDesign Research. London: Routledge Taylor and Francis Group.
Aksoy, G. (2012). The Effects of Animation Technique on the 7th Grade Science and Technology Course. Jurnal of Scientific Research. Vol.3, pp: 304-308, (Online), (http://www.SciRP.org/jornal/cc), diakses 30 Maret 2015.
Aljupri. (2008). Design Research on Computational Estimation for Grade Five Primary School Students in Indonesia. Prosiding KNM XIV Palembang. Palembang: Sriwijaya University.
Ashlock, R. B. 1994. Error Patterns in Computation. (6th ed). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Freudenthal, H. (1991). Revisiting Mathematics Education. China Lecture. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
Garlikov. 2004. The Concep and Teaching of Place Value, (Online), (http://www.garlikov.com/PlaceValue.h tml), diakses 26 Maret 2015.
Maria, G. 2011. Artacts and utilization schemes in mathematics teacher education: place value in early childhood education. J Math Teacher Educ (2011), DOI 10.007.
Maria, V & Becker. 1997. Children’s Developing Understanding of Place Value: SemioticAspets. Cognition and Instruction, 15(2), 265-286. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Negoro, S.T. & Harahap, B. 1983. Ensiklopedia Matematika. Jakarta: Ghalia Indonesia.
Novita, R. & Putra, M. 2012. Pemahaman Konsep Nilai Tempat dalam Mendukung Siswa Menyelesaikan Penjumlahan Bilangan Tiga Angka. Prosiding seminar nasional I, pp 183-192. Banda Aceh: Universitas Syiah Kuala
Payne, J. N. & Huinker, D. M. 1993. Early Number and Numeration; dalam Jensen, R.J. (Ed.), Reasearch Ideas for the Classroom: Early Childhood Mathematics. (hlm. 43—70). New York: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics Research Interpretation Project/Macmillan Publishing Company.
Prahmana, R.C.I. (2010). Permainan “Tepuk Bergilir” yang Berorientasi Konstruktivisme dalam Pembelajaran Konsep KPK Siswa Kelas IV A di SD N 21 Palembang. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika Volume 4 No. 2, pp. 61-69. Palembang: Universitas Sriwijaya
Reys, R. E., Suydam, M. N., Lindquist, M. M., & Smith, N. L. 1984. Helping Children Learn Mathematics. (5th ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Seputra, T. MHT & Amin, S. M. 1994. Matematika 1b: Mari Berhitung untuk Sekolah Dasar Kelas 1 Cawu 2. Jakarta: Depdikbud-Balai Pustaka.
Thomson. 2000. Teaching Place Value in UK: Time for Reapracial?. Educational Review. Vol 52, No 3, 2000. Department of Education, UK.
Zulkardi. (2002). Developing A Learning Environment on Realistic Mathematics Education for Indonesian Student Teachers. Published Dissertation. Enschede: Universityof Twente.