Main Article Content
Abstract
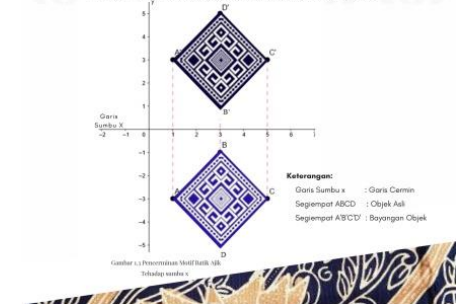
The ineffective use of constructivist learning through mathematical abstraction activities by teachers has led to low mathematics learning results. To promote mathematical abstraction, teaching materials must integrate the visualization of Minangkabau batik motifs. Therefore, this research aimed to describe the characteristics of teaching materials by adopting a 4D developmental model. The data analysis across the development stage included qualitative descriptive analysis for data received from interviews, observations, document reviews, and literature reviews, as well as quantitative descriptive analysis for data obtained from wide validation. The results showed that (1) Minangkabau batik motifs contained the concept of transformation geometry including reflection, rotation, translation, and dilation. (2) The characteristics of teaching materials included (a) having a cover, encouragement sheet, foreword, table of contents, materials, supporting information, exercises, assessments, and bibliography, (b) meeting the appropriateness of graphics, content, and language, (c) displaying the visualization of Minangkabau batik motifs for presentation of material, exploration of the properties of transformation geometry, and finding answers to prompting and practice questions, as well as (d) containing student activities in constructing concepts and making connections between such concepts. In conclusion, this research could help teachers improve students' mathematical abstraction using local cultures and teaching materials.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2024 Dona Afriyani, Lailatul Ramadhani, Isra Nurmai Yenti, Elda Herlina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles published Open Access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read and download. We are continuously working with our author communities to select the best choice of license options, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA).
References
- Afriyani, D. (2020). Development of leaflet based on the Bruner theory on the materials of the two-variable linear equation system [in Bahasa]. Matematika dan Pembelajaran, 8 (1), 74-86. https://doi.org/10.33477/mp.v8i1.1303
- Andriani, P, Kurniawati, K.R.A & Afriyani, D. (2022). A framework for assessing translation among multiple representations. Jurnal Teori dan Aplikasi Matematika (JTAM), 6(2), 321-330. https://doi.org/10.31764/jtam.v6i2.7193
- As’ari, A.R., Kurniati, D., & Subanji. (2019). Teachers’ expectation of students’ thinking processes in written works: A survey of teachers’ readiness in making thinking visible. Journal on Mathematics Education, 10 (3), 409-424. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.10.3.7978.409-424
- Budiman, P. M., Trimurtini, & Purwati, P. D. (2023). Implementing Bruner’s theory for the conceptual understanding of addition and subtraction. International Research-based Education Journal, 5(1), 119-127. http://dx.doi.org/10.17977/um043v5i1p119-127
- Daswarman & Sutadji, E. (2022). Minangkabau ethnomathematics in primary school mathematics learning [in Bahasa]. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Dasar, 6 (1), 16-20. https://doi.org/10.36928/jipd.v6i1.862
- Dewi, N. P. W. P. & Agustika, G. N. S. (2020). Effectiveness of mathematics learning through PMRI approach to mathematics knowledge competency [in Bahasa]. Jurnal Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pendidikan, 4(2), 204-214. https://doi.org/10.23887/jppp.v4i2.26781
- Fitriani, N., Suryadi, D., & Darhim, D. (2018). Analysis of mathematical abstraction on concept of a three-dimensional figure with curved surfaces of junior high school students. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1132(2018) 12037. 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1132/1/012037
- Fitriza, R., Afriyani, D., Turmudi, & Juandi, D. (2018). The exploration of ethno-mathematics embedded on traditional architecture of Rumah Gadang Minangkabau. 160 (Incomed 2017), 270–276. https://doi.org/10.2991/incomed-17.2018.57
- Hanik, U., Efendy, M., Jannah, A. N., & Fatmawati, I. (2024). Ethnomathematics: Exploration of mathematical concepts on the process of Madurese salt production. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(1), 59–78. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i1.pp59-78
- Hutagalung, E.E., Mulyana, E., & Pangaribuan, T.R. (2020). Mathematical abstraction: Students’ concept of triangles. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 1521 (032106). https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1521/3/032106
- Johar, R, Moulina, A. R, & Away, Y. (2024). Development of e-learning based remedial videos on fraction in middle school. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(1), 97-112. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i1.pp97-112
- Jariyah, A., Putri, R. I. I & Zulkardi. (2024). Development of learning video reflection using Palembang songket context to determine students' mathematical reasoning. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(2), 273-294. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i2.pp273-294
- Jawa Pos. Kemendikbudristek revealed average teacher competency score of 50.64 points [in Bahasa]. Page 1. Access on November 19, 2021 in address https://www.jawapos.com/pendidikan/01355273/kemendikbudristek-ungkap-ratarata-skor-kompetensi-guru-5064-poin
- Khasanah, N., Nurkaidah, D. R., & Prihandika, Y. A. (2019). Learners' mathematical abstraction process in view of spatial intelligence [in Bahasa]. Journal of Mathematics and Mathematics Education, 9(2). 77-87. https://dx.doi.org/10.20961/jmme.v9i2.48396
- Kusuma, J. K., Rachmad, I., & Hamidah. (2021). Constructivism from philosophy to mathematics learning. International Journal of Economy, Education and Entre preneurship, 1 (2). 58-63 https://doi.org/10.36928/jipd.v6i1.862
- Mitchelmore, M. C., & White, P. (2007). Abstraction in mathematics learning. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 19(2), 1-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03217452
- Mulyani, E. & Natalliasari, I. (2020). Ethnomathematical exploration of Sukapura batik [in Bahasa]. Mosharafa: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika. 9(1). 131-142. https://doi.org/10.31980/mosharafa.v9i1.598
- OECD. (2019). Pisa 2019 Results. PISA, OECD Publishing, Paris
- OECD. (2022). Pisa 2022 Results (Volume I) The state of learning and equity in education. PISA. OECD Publishing. Paris.
- Pathuddin, H. & Raehana, S. (2019). Ethnomathematics: Traditional Bugis food as a mathematics learning resource [in Bahasa]. MaPan: Jurnal Matematika dan Pembelajaran, 7 (2), 307-327. https://doi.org/10.24252/mapan.2019v7n2a10
- Permita, A. I., Nguyen, T., & Prahmana, R. C. I. (2022). Ethnomathematics on the Gringsing batik motifs in Javanese culture. Jurnal of Honai Math, 5 (2), 85-108. https://doi.org/10.30862/jhm.v5i2.265
- Piaget J. (1999). The construction of reality in the child. Psychology Press.
- Prahmana, R. C. I., & D'Ambrosio, U. (2020). Learning geometry and values from patterns: Ethnomathematics on the batik patterns of Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Journal on Mathematics Education, 11(3), 439-456.
- Rahmawati, Y. Z. (2020). Realistic mathematics approach with ethnomathematics of Minangkabau Gadang houses on Pythagorean theorem material [In Bahasa]. Jurnal Azimut, Edisi Khusus SMAR, 3(1), 22-29. https://doi.org/10.31317/jaz.v3iSMAR.636
- Rosmiati, R. N., & Ni’mah, K. (2021). Analysis of mathematical abstraction ability in terms of learning style Kolb assisted by Google Slides media. Jurnal Math Educator Nusantara: Wahana Publikasi Karya Tulis Ilmiah Di Bidang Pendidikan Matematika, 7(1), 26-36. https://doi.org/10.29407/jmen.v7i1.15675
- Rytilä, J. (2021). Social constructivism in mathematics? The promise and shortcomings of Julian Cole’s institutional account. Synthese, 2021(199),11517–11540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-021-03300-7
- Sa’dijah, C., Afriyani, D., Subanji, S., Muksar, M., & Anwar, L. (2014). Assessing students’ pseudo-mathematical translation using translation-verification model. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2014(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5054548
- Sampoerno, P. D., & Meiliasari, M. (2019). Analysis of the mathematical learning materials with the characteristics of realistic mathematics education in the design research pre-service teachers’ theses in Indonesia J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1402(7), 1-7, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1402/7/077105
- Salmon, A. K., & Barrera, M.X. (2021). Intentional question to promote thinking and learning. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 40 (100822).1-10, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2021.100822
- Sarita, R., & Kurniawati. Y. (2020). Development of students’ worksheets (LKPD) for chemistry based on science generic skills [in Bahasa]. Jurnal of The Indonesian Society of integrated Chemistry, 12(1), 31-39, https://doi.org/10.22437/jisic.v12i1.7846
- Skemp, R. R. (2012). The psychology of learning mathematics: Expanded American edition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc: New York. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203396391
- Syahriannur. (2019). Exploration of ethnomathematics of Minangkabau songket fabric to reveal the philosophical value of mathematical concepts [in Bahasa]. Jurnal Math Education Nusantara, 2 (1), 58-63. https://doi.org/10.54314/jmn.v2i1.69
- Thiagarajan, S., Semmel, D. S., & Semmel, M. I. (1974). Instructional Development for Training Teachers of Exceptional Children. Minneapolis, MN: Leadership Training Institute/Special Education, University of Minnesota.
- Tim Oates-Assessment Research & Development. 2015. Textbooks–What are the features of a good textbook. Cambridge: University of Cambridge.
- Ulumudin, I., Mardiansyah, & Joko, B.S. 2017. Textbooks and enrichment: Completeness and appropriateness of 2013 curriculum textbooks and policies for cultivating student reading interest [in Bahasa]. Jakarta: Pusat Penelitian Kebijakan Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Balitbang, Kemendikbud.
- UNESCO. (2015). Textbooks and other education materials: what key messages do we want to convey and how?. France: UNESCO.
- Van Oers, B., & Poland, M. (2007). Schematizing activities as a means for encouraging young children to think abstractly. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 19(2), 10-22. https://doi.org/10.54314/jmn.v2i1.69
- Liang, Y., & Cobern, W. W. (2013). Analysis of a typical Chinese high school biology textbook using the AAAS textbook standards. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 9(4), 329-336.
References
Afriyani, D. (2020). Development of leaflet based on the Bruner theory on the materials of the two-variable linear equation system [in Bahasa]. Matematika dan Pembelajaran, 8 (1), 74-86. https://doi.org/10.33477/mp.v8i1.1303
Andriani, P, Kurniawati, K.R.A & Afriyani, D. (2022). A framework for assessing translation among multiple representations. Jurnal Teori dan Aplikasi Matematika (JTAM), 6(2), 321-330. https://doi.org/10.31764/jtam.v6i2.7193
As’ari, A.R., Kurniati, D., & Subanji. (2019). Teachers’ expectation of students’ thinking processes in written works: A survey of teachers’ readiness in making thinking visible. Journal on Mathematics Education, 10 (3), 409-424. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.10.3.7978.409-424
Budiman, P. M., Trimurtini, & Purwati, P. D. (2023). Implementing Bruner’s theory for the conceptual understanding of addition and subtraction. International Research-based Education Journal, 5(1), 119-127. http://dx.doi.org/10.17977/um043v5i1p119-127
Daswarman & Sutadji, E. (2022). Minangkabau ethnomathematics in primary school mathematics learning [in Bahasa]. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Dasar, 6 (1), 16-20. https://doi.org/10.36928/jipd.v6i1.862
Dewi, N. P. W. P. & Agustika, G. N. S. (2020). Effectiveness of mathematics learning through PMRI approach to mathematics knowledge competency [in Bahasa]. Jurnal Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pendidikan, 4(2), 204-214. https://doi.org/10.23887/jppp.v4i2.26781
Fitriani, N., Suryadi, D., & Darhim, D. (2018). Analysis of mathematical abstraction on concept of a three-dimensional figure with curved surfaces of junior high school students. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1132(2018) 12037. 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1132/1/012037
Fitriza, R., Afriyani, D., Turmudi, & Juandi, D. (2018). The exploration of ethno-mathematics embedded on traditional architecture of Rumah Gadang Minangkabau. 160 (Incomed 2017), 270–276. https://doi.org/10.2991/incomed-17.2018.57
Hanik, U., Efendy, M., Jannah, A. N., & Fatmawati, I. (2024). Ethnomathematics: Exploration of mathematical concepts on the process of Madurese salt production. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(1), 59–78. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i1.pp59-78
Hutagalung, E.E., Mulyana, E., & Pangaribuan, T.R. (2020). Mathematical abstraction: Students’ concept of triangles. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 1521 (032106). https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1521/3/032106
Johar, R, Moulina, A. R, & Away, Y. (2024). Development of e-learning based remedial videos on fraction in middle school. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(1), 97-112. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i1.pp97-112
Jariyah, A., Putri, R. I. I & Zulkardi. (2024). Development of learning video reflection using Palembang songket context to determine students' mathematical reasoning. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 18(2), 273-294. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.v18i2.pp273-294
Jawa Pos. Kemendikbudristek revealed average teacher competency score of 50.64 points [in Bahasa]. Page 1. Access on November 19, 2021 in address https://www.jawapos.com/pendidikan/01355273/kemendikbudristek-ungkap-ratarata-skor-kompetensi-guru-5064-poin
Khasanah, N., Nurkaidah, D. R., & Prihandika, Y. A. (2019). Learners' mathematical abstraction process in view of spatial intelligence [in Bahasa]. Journal of Mathematics and Mathematics Education, 9(2). 77-87. https://dx.doi.org/10.20961/jmme.v9i2.48396
Kusuma, J. K., Rachmad, I., & Hamidah. (2021). Constructivism from philosophy to mathematics learning. International Journal of Economy, Education and Entre preneurship, 1 (2). 58-63 https://doi.org/10.36928/jipd.v6i1.862
Mitchelmore, M. C., & White, P. (2007). Abstraction in mathematics learning. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 19(2), 1-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03217452
Mulyani, E. & Natalliasari, I. (2020). Ethnomathematical exploration of Sukapura batik [in Bahasa]. Mosharafa: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika. 9(1). 131-142. https://doi.org/10.31980/mosharafa.v9i1.598
OECD. (2019). Pisa 2019 Results. PISA, OECD Publishing, Paris
OECD. (2022). Pisa 2022 Results (Volume I) The state of learning and equity in education. PISA. OECD Publishing. Paris.
Pathuddin, H. & Raehana, S. (2019). Ethnomathematics: Traditional Bugis food as a mathematics learning resource [in Bahasa]. MaPan: Jurnal Matematika dan Pembelajaran, 7 (2), 307-327. https://doi.org/10.24252/mapan.2019v7n2a10
Permita, A. I., Nguyen, T., & Prahmana, R. C. I. (2022). Ethnomathematics on the Gringsing batik motifs in Javanese culture. Jurnal of Honai Math, 5 (2), 85-108. https://doi.org/10.30862/jhm.v5i2.265
Piaget J. (1999). The construction of reality in the child. Psychology Press.
Prahmana, R. C. I., & D'Ambrosio, U. (2020). Learning geometry and values from patterns: Ethnomathematics on the batik patterns of Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Journal on Mathematics Education, 11(3), 439-456.
Rahmawati, Y. Z. (2020). Realistic mathematics approach with ethnomathematics of Minangkabau Gadang houses on Pythagorean theorem material [In Bahasa]. Jurnal Azimut, Edisi Khusus SMAR, 3(1), 22-29. https://doi.org/10.31317/jaz.v3iSMAR.636
Rosmiati, R. N., & Ni’mah, K. (2021). Analysis of mathematical abstraction ability in terms of learning style Kolb assisted by Google Slides media. Jurnal Math Educator Nusantara: Wahana Publikasi Karya Tulis Ilmiah Di Bidang Pendidikan Matematika, 7(1), 26-36. https://doi.org/10.29407/jmen.v7i1.15675
Rytilä, J. (2021). Social constructivism in mathematics? The promise and shortcomings of Julian Cole’s institutional account. Synthese, 2021(199),11517–11540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-021-03300-7
Sa’dijah, C., Afriyani, D., Subanji, S., Muksar, M., & Anwar, L. (2014). Assessing students’ pseudo-mathematical translation using translation-verification model. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2014(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5054548
Sampoerno, P. D., & Meiliasari, M. (2019). Analysis of the mathematical learning materials with the characteristics of realistic mathematics education in the design research pre-service teachers’ theses in Indonesia J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1402(7), 1-7, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1402/7/077105
Salmon, A. K., & Barrera, M.X. (2021). Intentional question to promote thinking and learning. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 40 (100822).1-10, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2021.100822
Sarita, R., & Kurniawati. Y. (2020). Development of students’ worksheets (LKPD) for chemistry based on science generic skills [in Bahasa]. Jurnal of The Indonesian Society of integrated Chemistry, 12(1), 31-39, https://doi.org/10.22437/jisic.v12i1.7846
Skemp, R. R. (2012). The psychology of learning mathematics: Expanded American edition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc: New York. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203396391
Syahriannur. (2019). Exploration of ethnomathematics of Minangkabau songket fabric to reveal the philosophical value of mathematical concepts [in Bahasa]. Jurnal Math Education Nusantara, 2 (1), 58-63. https://doi.org/10.54314/jmn.v2i1.69
Thiagarajan, S., Semmel, D. S., & Semmel, M. I. (1974). Instructional Development for Training Teachers of Exceptional Children. Minneapolis, MN: Leadership Training Institute/Special Education, University of Minnesota.
Tim Oates-Assessment Research & Development. 2015. Textbooks–What are the features of a good textbook. Cambridge: University of Cambridge.
Ulumudin, I., Mardiansyah, & Joko, B.S. 2017. Textbooks and enrichment: Completeness and appropriateness of 2013 curriculum textbooks and policies for cultivating student reading interest [in Bahasa]. Jakarta: Pusat Penelitian Kebijakan Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Balitbang, Kemendikbud.
UNESCO. (2015). Textbooks and other education materials: what key messages do we want to convey and how?. France: UNESCO.
Van Oers, B., & Poland, M. (2007). Schematizing activities as a means for encouraging young children to think abstractly. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 19(2), 10-22. https://doi.org/10.54314/jmn.v2i1.69
Liang, Y., & Cobern, W. W. (2013). Analysis of a typical Chinese high school biology textbook using the AAAS textbook standards. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 9(4), 329-336.